Identity and Identifier Terms and Concepts
An identifier is data used to identify something, such as a person, mobile device, computer browser, or household. See the sections below for information on the identity and identifier terms and concepts used at LiveRamp.
LiveRamp uses identifiers (such as name and postal address, email address, phone, RampIDs, cookie IDs, or mobile device IDs) to match your records to other identifiers in our Identity Graph.
Note
These might also be referred to as “Identifier data”.
The two main categories of identifiers are:
Known identifiers (identifiers which have been derived from, and/or can be associated with, PII). Identifiers in this category include name and postal address, email address, phone number, client customer IDs, AbiliTec Links, LiveRamp Known IDs, and (in some cases) custom IDs - see "Known Identifiers" for more information. Known identifiers are sometimes also referred to as "offline identifiers".
Pseudonymous identifiers (identifiers that can't be directly tied back to an individual on their own, such as known identifiers that have been pseudonymized and device identifiers). Identifiers in this category include cookie IDs, mobile device IDs, CTV IDs, IP addresses, and (in some cases) custom IDs - see "Pseudonymous Identifiers" for more information. Pseudonymous identifiers are sometimes also referred to as "online identifiers".
See "Formatting Identifiers" for more information on formatting known and pseudonymous identifiers. For a list of identifiers that LiveRamp supports and for information on identitier types (such as maintained and derived identifiers), see "Supported Identifier Types".
Warning
To prevent re-identification, do not combine known identifiers and pseudonymous identifiers in a single file or table that you send to LiveRamp for ingestion.
Caution
Stay consistent! Files for ingestion in the same LiveRamp should always have the same set of identifier fields, and the field names (headers in a column-based file and keys in a key-value file) and key should be consistent from file to file.
Note
For EU and UK customers, "personally-identifiable information" (or PII) is called “directly identifiable personal data”.
Known Identifiers
Known identifiers include PII identifiers and other identifiers that have been derived from, and/or can be associated with, PII and have not been pseudonymized yet.
In addition to PII-based identifiers (such as name and postal address or email address), known identifiers also include AbiliTec Links, LiveRamp Known IDs, client customer IDs, and (in some cases) custom IDs.
Note
Known identifiers and PII identifiers are sometimes referred to as "offline identifiers."
For a list of the known identifiers that can be included in LiveRamp workflows, see the table below:
Identifier | Notes | Embedded Identity Workflows | Activation and Other Workflows |
|---|---|---|---|
Name and postal addresses | Name and postal, or "NAP" | For formatting information, see the articles in “Embedded Identity in Cloud Environments”. | When using name and postal as an identifier, all required name and postal elements must be included in each record: first name, last name, street address, city, state, and ZIP. |
Email addresses | Can be plaintext or hashed, with SHA-256, MD5, and SHA-1 hashes accepted. | Can be plaintext or hashed, with SHA-256, MD5, and SHA-1 hashes accepted. | |
Phone numbers | Phone numbers can be used for matching by themselves or in combination with first and last name for greater accuracy. | Only plaintext is accepted. | Can be plaintext or hashed, with SHA-1 hashes accepted. |
Custom IDs (CIDs) | Your internal customer ID (also sometimes referred to as "Client Customer IDs"). | ||
AbiliTec Links | The Link format of the identifier tied to a record in our known identity graph. | AbiliTec Links can be generated through configuration options (for more information, see “Embedded Identity in Cloud Environments”). | For some use cases, AbiliTec Links can be ingested for activation use cases. Check with your LiveRamp account team for more information. |
LiveRamp Known IDs | The Known ID format of the identifier tied to a record in our known identity graph. | Known IDs are the default identifier returned through Embedded Identity workflows (for more information, see “Embedded Identity in Cloud Environments”). | Known IDs are the primary identifier used for data collaboration use cases. |
PII Identifiers
A category of identifiers where the identifiers consist of PII (personally identifiable information).
Note
For EU and UK customers, "personally-identifiable information" (or PII) is called “directly identifiable personal data”.
PII identifiers are a subset of the category of known identifiers, which are identifiers that have been derived from, and/or can be associated with, PII (and are therefore considered PII) and have not been pseudonymized yet. See "Known Identifiers" for more information.
Note
PII identifiers are sometimes also referred to as "offline identifiers."
Custom IDs (CIDs)
When used as input identifiers, CIDs (custom IDs) are the custom identifiers that you use to deduplicate records within your systems. When a CID is tied to PII in a file, it is considered a known identifier.
Note
In some cases, CIDs are identifiers that are assigned to users by a specific platform, such as Google or Facebook. LiveRamp often uses these types of identifiers as a cross-reference between a LiveRamp partner's ID and LiveRamp's IDs.
When a CID is tied to a RampID or another pseudonymous identifier, it is considered a pseudonymous identifier.
For more information, see "Formatting Custom IDs".
AbiliTec Links
An AbiliTec Link is considered a "known identifier" because it is tied to a record in our known identity graph. AbiliTec Links are generated and encoded for specific LiveRamp clients.
AbiliTec Link Types
There are three main types of AbiliTec Links:
ConsumerLinks: Represent an individual, based on PII
HouseholdLinks: Represent adults living together at the same location with a persistent relationship based on PII
AddressLinks: Represent a site or physical location
AbiliTec Link Versions
All Link types can come in maintained or derived versions, depending on whether or not they match with a record in the graph.
Maintained Links are returned when we have a match for the input data in the Known Identity Graph. These IDs are maintained in the graph, and so are persistent.
Derived Links, unlike maintained links, are not maintained in the Known Identity Graph. They are algorithmically derived based on the client input data. The same touchpoint will consistently output the same derived link on input.
Structure of AbiliTec Links
See the image and table below for a breakdown of the structure of an AbiliTec Link:
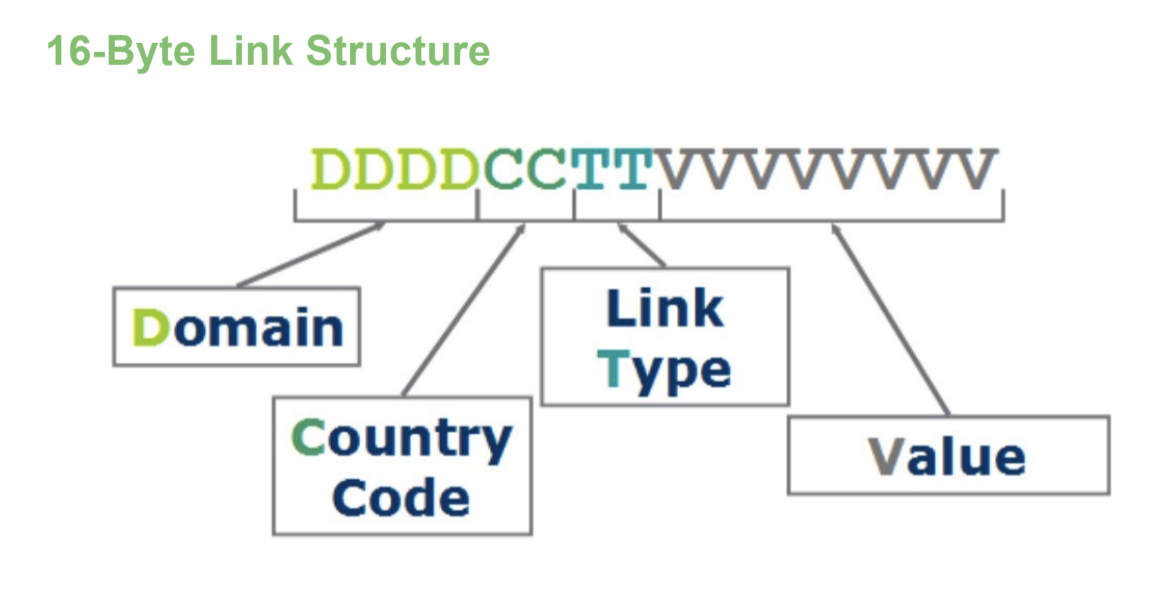
Link Part | Description | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Domain | Specifies the encoding value | 4 alphanumeric characters | T001 |
Country Code | Code for country graph matching to | 2 numeric digits (ISO-2 Country Standard) ZZ is used when ISO-2 does not assign a Country Code | US |
Link Type | Distinguishes the type of link – Maintained, Derived, Consumer, Address, etc. | 2 numeric digits | 01 |
Value | This represents the value portion of the link | 8 alphanumeric characters | abcd1234 |
Using AbiliTec Links
AbiliTec Links can be used in a client's environment for deduplication, person and household formation and validation, and data unification of identity fragments for known data sets.
Accessing AbiliTec Links
The best way to access AbiliTec Links from LiveRamp today is by using the AbiliTec API, which is a real-time, transactional API for resolving customer data (PII) to AbiliTec IDs. See our AbiliTec API help content and API reference and contact your LiveRamp representative to get started.
LiveRamp Known IDs
A LiveRamp Known ID is also considered a "known identifier" as it is tied to a record in LiveRamp’s Known Identity Graph and can sit next to PII.
Known ID Types
There are three main types of Known IDs:
Person IDs: Represent an individual, based on PII.
Household IDs: Represent adults that live and move together.
Place IDs: Represent a physical location.
Known ID Versions
All Known ID types can come in maintained or derived versions, depending on whether or not they match with a record in the graph:
Maintained Known IDs are returned when we have a match for the input data in the Known Identity Graph. These IDs are maintained in the graph, and so are persistent. A maintained Known ID will have a country code other than "ZZ" (such as "US").
Derived Known IDs, unlike maintained Known IDs, are not maintained in the Known Identity Graph. They are algorithmically derived based on the client input data. The same touchpoint will consistently output the same derived Known ID on input.
A derived Known ID will have a country code of "ZZ".
Structure of Known IDs
See the image and table below for a breakdown of the structure of a Known ID:
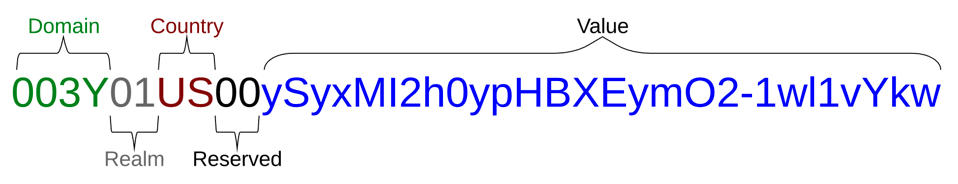
ID Part | Description | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Domain | Unique customer domain encoding code for IDs | 4 digits | T321 |
Realm | Identity Space or environment in which IDs will be stored (known realm is 00) | 2 digits | 00 |
Country Code | Each country has a distinct graph in order to maintain compliance in each market. For derived Known IDs, this will be "ZZ". | 2-digit ISO code | US |
Reserved | This space in the ID is reserved for future use cases | 2 digits | 00 |
Value | Unique value that represents associated data | 28 digit | See below |
Known IDs do not contain any of the following information:
Document class
Bundle information
Attribute values from the document
Request parameter values
Anything specific about the type of request that returned the document ID
Using Known IDs
LiveRamp Known IDs allow you to consolidate your consumer PII across fragmented data sources into a unified view to gain an accurate customer profile, improving customer data management and powering effective customer engagement.
Accessing Known IDs
The best way to access Known IDs is through our Embedded Identity products for customers in Snowflake and AWS. For more information, see "Embedded Identity in Cloud Environments".
Pseudonymous Identifiers
Pseudonymous identifiers are identifiers, such as known identifiers that have been pseudonymized or device identifiers (such as a mobile device ID or cookie ID), that can't be directly tied back to an individual.
In addition to device-based identifiers, pseudonymous identifiers include RampIDs and (in some cases) custom IDs.
Note
Pseudonymous identifiers and device-based identifiers are sometimes referred to as "online identifiers".
These identifiers can include:
Cookies: Data that is set by a website when a particular user’s browser visits that site. See "Formatting Cookies" for more information.
CTV IDs: Device identifiers associated with Connected TVs. See "Formatting CTV IDs" for more information.
Custom IDs (CIDs): Identifiers that are assigned to users by a specific platform, such as Google or Facebook. See "Formatting Custom IDs" for more information.
Note
If a custom ID is tied to PII, such as a custom identifier that you use to deduplicate records within your systems, it is considered "known" and not "pseudonymous."
Mobile device IDs: Identifiers that identify a particular mobile device, such as Identifier for Advertisers (IDFAs) for iOS (Apple) devices and Android Advertising IDs (AAIDs) for Android devices. These can be plaintext or hashed, with SHA-1 hashes accepted. See "Formatting Mobile Device IDs" for more information.
Note
Web browsing (cookie) data from mobile devices is considered web data and is not included in the mobile category.
IP addresses (Internet Protocol addresses): Identifiers assigned to each device connected to a network (like the internet).
RampIDs: LiveRamp’s identifier that is tied to devices in the LiveRamp Identity Graph. See "Formatting RampIDs" for more information.
Caution
We have a 90-day retention window for cookie IDs and a 2-year retention window for mobile device IDs.
Note
Generally speaking, LiveRamp can accept cookies and custom IDs as input from any platform to which it can distribute data (some exceptions do exist; contact your LiveRamp representative with specific questions).
Mobile Device IDs
Unique identifiers given to mobile devices. Types of mobile device IDs include:
Identifier for Advertisers (IDFA) for Apple/iOS devices
Android Advertising ID (AAID) for Android devices
This category of IDs is sometimes referred to as Mobile User IDs (MUIDs) or Mobile Advertising IDs (MAIDs).
For more information, see "Formatting Mobile Device IDs".
CTV IDs
CTV IDs are device identifiers associated with Connected TVs.
For more information, see "Formatting CTV IDs".
Note
If you're going to be sending CTV IDs, we recommend that you set up a CTV ID sync before sending CTV IDs to increase your match rates. CTV ID syncs can be accomplished via event files or via pixel. For more information, see the articles listed below:
Custom IDs (CIDs)
In some cases, CIDs are identifiers that are assigned to users by a specific platform, such as Google or Facebook. LiveRamp often uses these types of identifiers as a cross-reference between a LiveRamp partner's ID and LiveRamp's IDs. When it is tied to a RampID or another pseudonymous identifier, it is considered a pseudonymous identifier.
Note
In other cases CIDs are your custom identifiers that you use to deduplicate records within your systems. When a CID is tied to PII in a file, it is considered a known identifier.
For more information, see "Formatting Custom IDs".
IP Addresses
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique number assigned to each device connected to a network (like the internet).
Note
For LiveRamp workflows, IP addresses are only supported for mapping files, measurement, and targeting for CTV, podcasting, gaming, and IoT only.
RampIDs
In the context of identifiers, a RampID is LiveRamp's universal, pseudonymous identifier that is tied to devices in the LiveRamp Identity Graph. It is a pseudonymized version of an AbiliTec ID, which is based on PII.
RampID Types
There are several types of RampIDs:
An Individual RampID represents an individual. It is a pseudonymized version of an AbiliTec Person ID which is based on PII. The length of these RampIDs, and the characters they start with, depends on whether they are maintained or derived versions (see below).
A Household RampID represents adults living together at the same location who exhibit a persistent relationship. It is a pseudonymized version of an AbiliTec Household ID which is based on PII. These RampIDs are 49 characters long and start with "hY".
A Placeholder Cookie RampID is an identifier provided for a cookie ID that LiveRamp has not yet identified. These RampIDs are 49 characters long and start with "Xc".
A Placeholder Mobile RampID is an identifier provided for a mobile device ID which LiveRamp has not yet identified. These RampIDs are 49 characters long and start with "Xm".
RampID Versions
Individual RampIDs come in maintained versions and derived versions, depending on whether there is a maintained record in the AbiliTec Identity Graph for the input data provided:
A maintained RampID represents a person that LiveRamp can fully recognize. Maintained RampIDs are 49 characters long and start with "XY." For example, "XY1005wXyWPB1SgpMUKIpzA0I3UaLEz-2lg0wFAr1PWK7FMhs."
A derived RampID is generated from the input PII provided when there is no maintained record for the input data. Derived RampIDs are 70 characters long, and start with "Xi." For example, "Xi1005p_iYcKP7ZlvFwwK9EwR8GKl_VJqIWUhEaAFmHLAjNOQ9b6OQzSkA43XiVFcTYQ9X."
More Information About RampIDs
RampIDs are LiveRamp’s people-based, cross-device identifiers that you’ll use to communicate with LiveRamp and collaborate with partners. A RampID is a privacy-safe, online representation of an individual, built by deterministically merging offline PII (personally identifiable information, such as email address, name, postal address, and phone number) and matching to cookies, mobile device IDs, and proprietary platform IDs.
See the articles below for more information about RampIDs:
"RampID Methodology" for information on how RampIDs are created, and how LiveRamp’s identity graph functions on the whole.
"Interpreting RampID, LiveRamp's People-Based Identifier" for information on how to interpret RampIDs.
"RampID's Deterministic Standards vs. Probabilistic, Cross-Device Matching"
Supported Identifier Types
LiveRamp supports the following identifier types:
PII: Personally identifiable information, including name and postal, email, phone, and hashed email.
Example: name@gmail.com
Note
For EU and UK customers, this type of identifier data is called “directly identifiable personal data”.
RampID: LiveRamp’s universal, encrypted identifiers that LiveRamp customers and partners receive.
Example: XY1000r99GR8_vGdKIEZt98TLMY6RKCI3kYrEdaM3SF0twCqN
Cookie: A partner cookie in sync with LiveRamp.
Example: 134c3ef6-19af-469f-940f-46f948491f8e
Note
Partner cookie IDs can be in many different formats.
IDFA or AAID: Pseudonymous mobile device identifiers, such as Apple's ID for Advertising (IDFA) for iOS devices and Google's Android Advertiser ID (AAID) for Android devices.
Example: 6219dbf3d457cf1419bd855e21ea247ac4b08949
CTV IDs: Device identifiers associated with Connected TVs.
Custom ID: An account-based user ID understood by LiveRamp.
Example: 535c3ef6-19af-469f-940f-46f948491f8e
Note
Partner custom IDs can be in many different formats.
Note
For formatting information, see "Formatting Identifiers".
Maintained Identifiers
In the context of LiveRamp, a maintained identifier (such as a maintained RampID or a maintained AbiliTec ID) represents a person that LiveRamp can fully recognize.
A maintained identifier is the identifier associated with a given record when there is a maintained record in the AbiliTec Identity Graph (our PII-based offline identity graph) for the input data provided.
Multiple online devices can usually be matched to a maintained RampID, enabling cross-device use cases.
In some cases, there might be more than one maintained identifier for a given record. This situation sometimes arises when a particular PII touchpoint is present in more than one maintained record in the Identity Graph.
Note
What if there isn't a maintained record for the input data? If there is no maintained record in the AbiliTec Identity Graph, LiveRamp generates a derived identifier for each PII touchpoint, such as a derived AbiliTec ID or RampID.
As new information is added to the AbiliTec Identity Graph over time, a maintained identifier might change to reflect that new information.
Tip
How should updates be handled? LiveRamp does not provide mappings of old RampIDs to new RampIDs, or provide notice that a transition has occurred. This can be handled by simply overwriting the RampID you have in your system tied to a given device/user with the new RampID while maintaining data you had previously associated to that device/user.
Derived Identifiers
In the LiveRamp context, a derived identifier is associated with a known PII touchpoint (such as an email address or phone number) when there is no maintained record in the AbiliTec Identity Graph (our PII-based offline identity graph) for the provided input data. Derived identifiers include derived RampIDs and derived AbiliTec IDs.
If there is a maintained record in the AbiliTec Identity Graph, LiveRamp will associate a maintained identifier, such as a maintained AbiliTec ID or a maintained RampID, with that record.
Multiple online devices can usually be matched to a derived RampID, enabling cross-device use cases.
As PII is added to the AbiliTec Identity Graph, a derived identifier can be converted to a maintained identifier once we can confidently resolve those PII touchpoints to an individual.
Tip
How should updates be handled? LiveRamp does not provide mappings of old derived RampIDs to new maintained RampIDs, or provide notice that a transition has occurred. This can be handled by simply overwriting the RampID you have in your system tied to a given device or PII with the new RampID while maintaining data you had previously associated to that device or PII.
Placeholder Identifiers
In the context of LiveRamp, a placeholder cookie RampID or placeholder mobile RampID is the identifier provided for a cookie or mobile device ID which LiveRamp has not identified. Providing a placeholder identifier ensures that every device ID has a corresponding RampID, and allows LiveRamp to update to a maintained RampID if the device ID is identified in the future.