Getting Started with Media Intelligence for Publishers
LiveRamp Clean Room’s Media Intelligence allows publishers to provide brands with critical media performance insights to quickly start collaboration.
Media Intelligence typically includes the following types of insights:
Audience Overlaps and Indices
Optimal Reach and Frequency
Attribution (First, Last, and Linear)
For more information on the specific insights available, see the "Run Reports" section below.
To learn more about the insights included in Media Intelligence, click here.
Collaborating with brands involves working with LiveRamp to develop a clean room template that contains the questions and reports that you’ll make available to the brands you work with. After you connect your datasets to your account and to the questions in the template, you then generate a clean room for each brand to use for collaboration, with your data filtered so that each brand only sees the data that applies to them.
Note
Before starting the collaboration, talk to the brand so that they understand how reports can be generated and accessed (you can allow brands to run reports and view insights in LiveRamp Clean Room, or you can run the reports yourself and deliver the insights to the brand). This is typically handled during LiveRamp’s “matchmaking” process.
Overall Steps
Implementing Media Intelligence for publishers typically involves the following overall steps:
If you’re a new LiveRamp Clean Room customer:
You sign the required agreements.
You work with the LiveRamp Clean Room team on making key implementation decisions.
LiveRamp creates a Clean Room account for you and populates it with a Media Intelligence clean room template that you’ll use to generate clean rooms for your brands.
You prepare your data.
You connect your datasets by creating data connections to each dataset.
You edit the Media Intelligence clean room template:
You make any needed edits to parameters and question permissions.
You assign your datasets to each question in the template.
You generate a clean room from the template for the brand.
You edit the clean room configuration for your exposures dataset to restrict the values to show only data relevant for that brand.
You send an invitation to the brand to join the clean room.
The brand connects their datasets, provisions those datasets to the clean room, and then assigns the datasets to the questions.
You or the brand run reports (depending on the arrangement with the brand).
The brand accesses reports (depending on the arrangement with the brand, this might be done in LiveRamp Clean Room or you might send them to the brand).
For more information on performing these steps, see the sections below. For new LiveRamp Clean Room publisher customers, see “Getting Started with LiveRamp Clean Room for Publishers” for the steps required for new customers.
Prepare Your Data
For your Media Intelligence clean rooms, you’ll need to connect the following types of datasets:
Exposures dataset (containing exposures/impressions, also known as “ad logs”)
Publisher Audience dataset (with data on user segments in your platform)
Note
LiveRamp will prepare and connect your CID | RampID mapping dataset.
We recommend that your exposures dataset contain data on all brands and that you then apply a brand filter for each brand’s clean room so that the brand only sees their data. That way you only have to create one data connection for that dataset. You can connect individual exposures datasets that only contain data on individual brands, but then you’ll need to create a separate exposures dataset data connection for each brand.
When preparing your data for Media Intelligence clean rooms, make sure to follow the guidelines for file and table names, folder names, and headers for files and tables listed in “Guidelines for Standard Dataset Headers, File Names, and Folder Names” as well as the general formatting information in “Format Your Clean Room Data”.
Note
If you’re unable to format your data as presented below, you can perform certain data transformations when you provision the dataset to the clean room (such as changing a field’s data type, transforming a timestamp format, or adding a field that is not present in your data). For more information, see “Perform Dataset Transformations".
Prepare Your Exposures Dataset
When preparing your exposures dataset, make sure it includes the required fields shown below, with the correct data type for each field:
Field Contents | Recommended Field Name | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
A unique user ID |
| string |
Unique identifier for the event |
| string |
Name of the brand |
| string |
Name of the campaign |
| string |
Type of event |
| string |
Timestamp of the exposure event (ideally in UTC ISO8601 format: “ YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ssZ”) |
| timestamp |
For information on formatting of additional fields you might include in your exposures dataset, see "Format an Exposures Dataset".
Prepare Your Publisher Audience Dataset
When preparing your publisher audience dataset, make sure it includes the required fields shown below, with the correct data type for each field:
Field Contents | Recommended Field Name | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
A unique user ID |
| string |
Unique identifier of audience segment used for targeting this impression |
| string |
The name of the segment |
| string |
The name of the category |
| string |
Connect Your Data
Once you've confirmed that you have the required datasets ready for use, you're ready to connect your data. If you’re going to be hosting your data at its source in a cloud warehouse, you’ll need to connect that data to your Clean Room account.
Note
These data connections can be used for multiple Media Intelligence clean rooms.
If you’ve chosen to have LiveRamp host the data, skip these steps and see the information in “Uploading Data”.
Before configuring your data connections in LiveRamp Clean Room, confirm you have the required datasets ready for use in a Media Intelligence clean room. Knowing where your datasets live, the credentials and tables required to access those datasets, and having the proper file and table formatting in place will make the remainder of your setup much more seamless. For more information, see the "Prepare Your Data" section above.
Connecting your data involves creating a data connection in LiveRamp Clean Room by performing the overall steps listed below. The type of connection to create will depend on your situation and business needs. Your LiveRamp representative will work with you to determine the type(s) of connections to create.
A data connection needs to be created for each dataset you want to utilize in a clean room, so you will need separate data connections for your exposures dataset and your publisher audience dataset.
For more information on the steps to perform for your cloud provider, see the articles in “Connect to Cloud-Based Data”. Specific instructions for each step will be listed in the appropriate help article for your data connection type.
Media Intelligence clean rooms are Hybrid-type clean rooms, so make sure to follow the instructions for the appropriate data connection type that supports Hybrid clean rooms:
After you create data connections, these connections appear on the Data Connections page, and you can then provision those datasets to your Media Intelligence clean rooms.
Edit the Media Intelligence Template
You might want to modify the data control parameters or question permissions in the Media Intelligence template that LiveRamp populated in your account.
Note
If you want to customize data control parameters or question permissions by brand, you can do that when you generate the clean room from the template for the brand.
From the navigation menu, select Clean Room → Clean Rooms to open the Clean Rooms page.
Select the Templates tab.
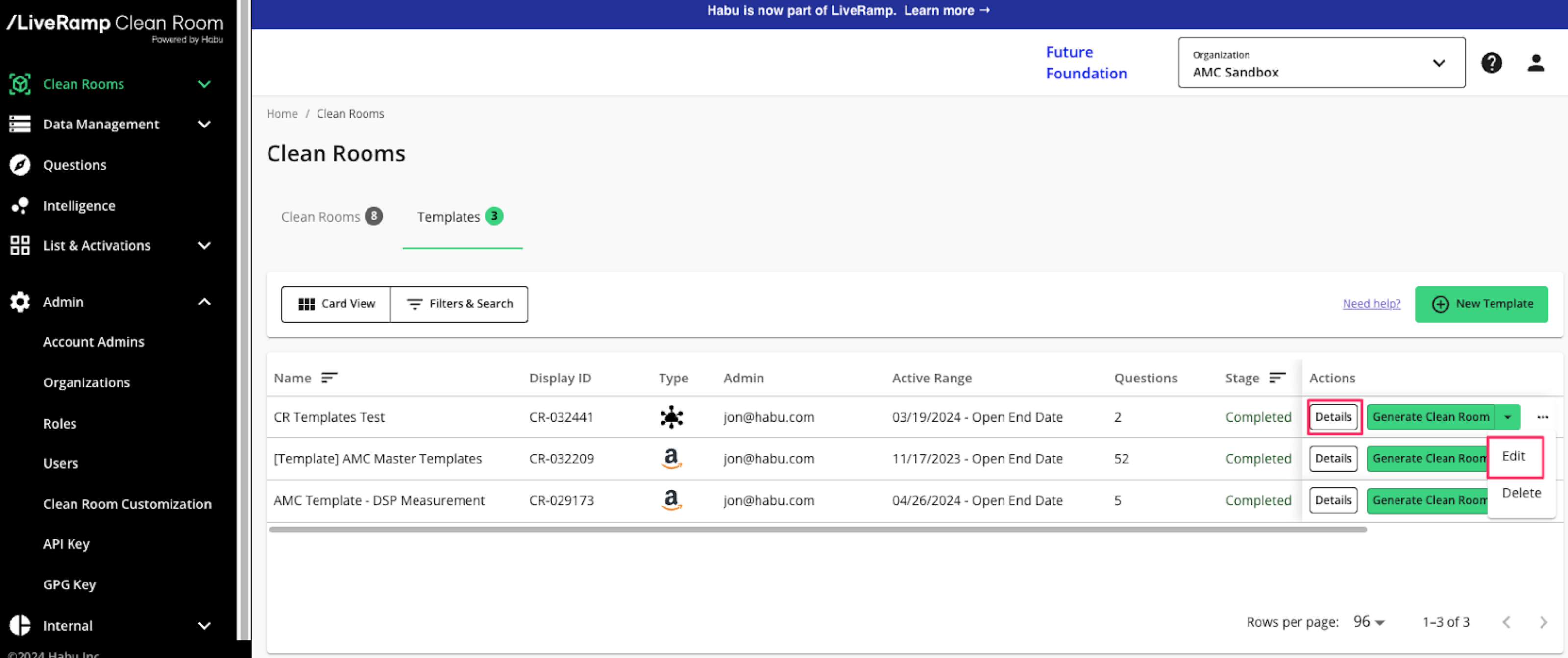
From the More Actions menu (three dots) for the Media Intelligence template, select Edit.
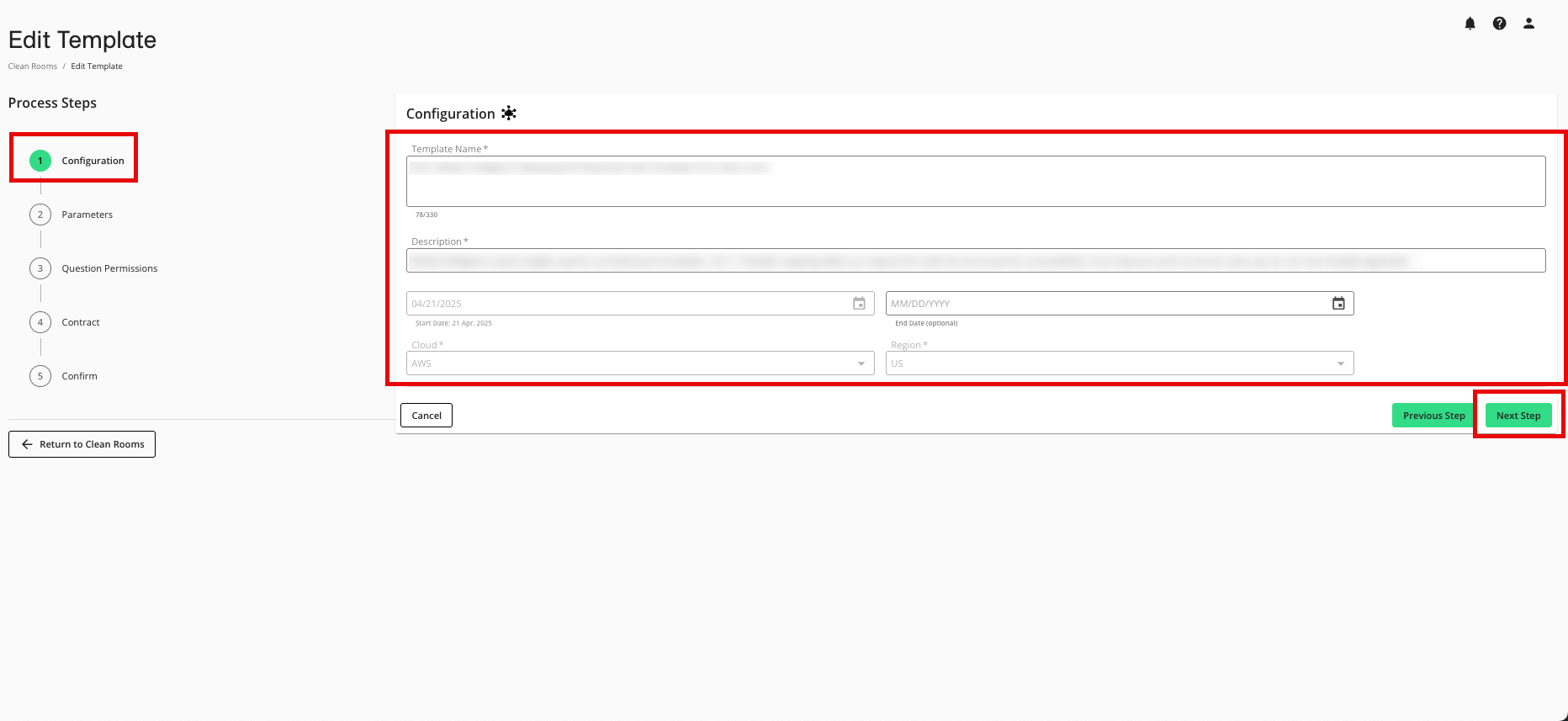
From the Configuration step, make any desired edits and then click Next Step.
From the Parameters step, make any desired edits and then click Next Step.
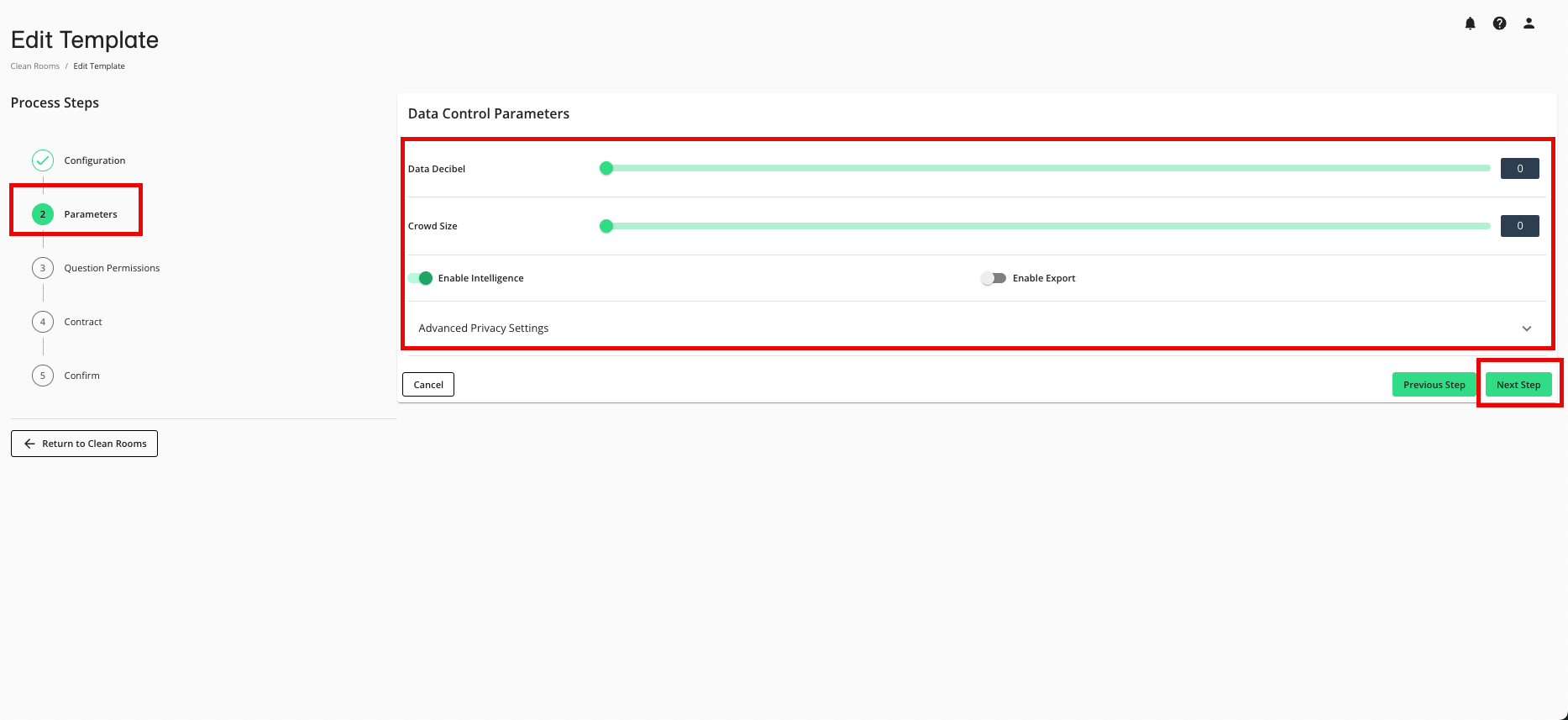
Data decibel (also referred to as "noise"; for more information see "Noise Injection Using Laplacian Noise")
Crowd size (also referred to as "k-min threshold"; for more information, see "K-min Results Output Enforcement")
Enable Intelligence
Enable Export: Slide the toggle to the right to enable an export of results to an outside cloud location, like an AWS S3 location or GCS (for more information, see "Export Results to a Cloud")
From the Question Permissions step, make any desired edits and then click .
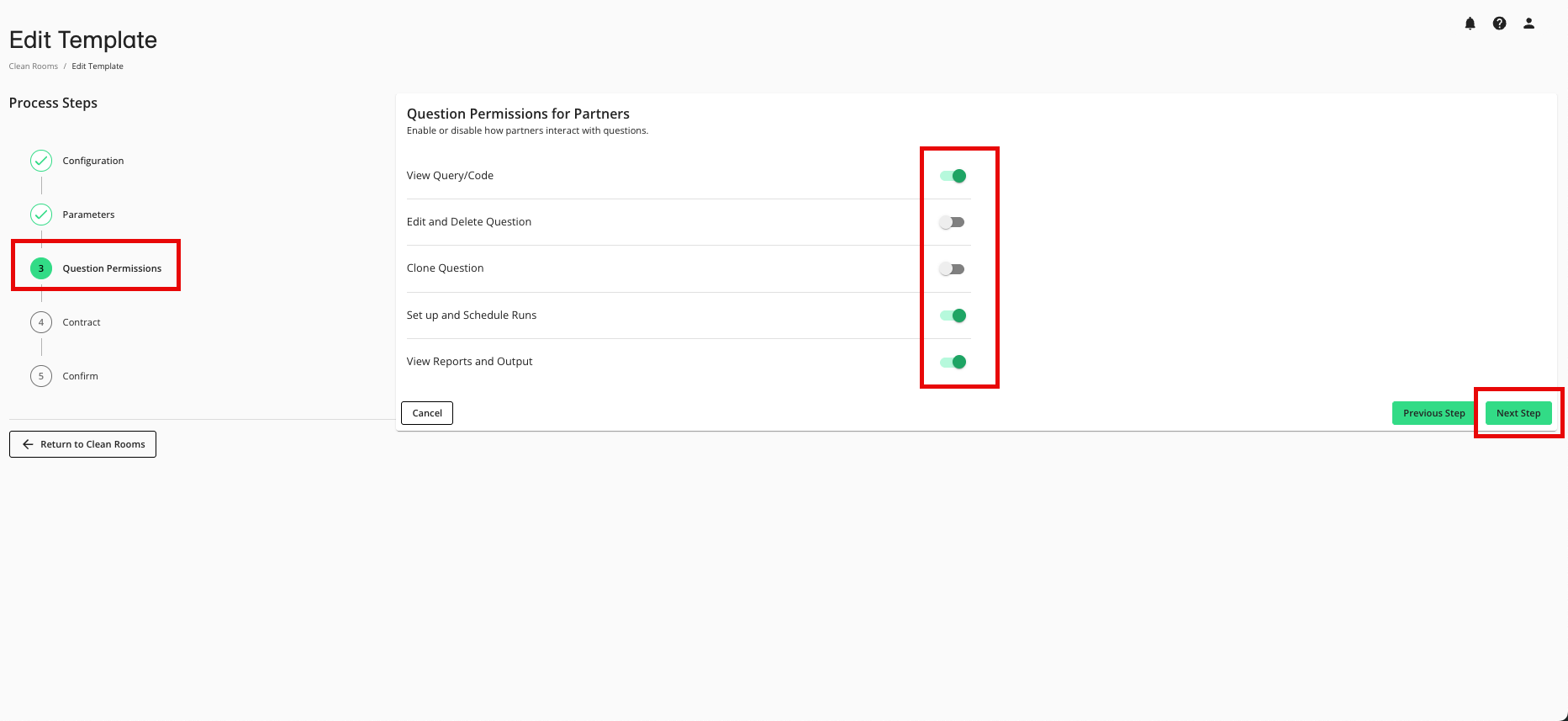
View Query/Code: Allows partners to view the code for the question prior to opting datasets into the question.
Edit and Delete Question: Allows partners to edit the content of questions or delete them from the clean room if they are no longer required.
Clone Question: Allows partners to create a clone of the question and assume ownership of the clone. This means partners in the clean room can edit the cloned version of the question.
Set up and Schedule Runs: Allows partners to trigger runs of the question and schedule them on a recurring basis.
View Reports and Output: Allows partners to view the results of a given question run for the specified question. You can choose to apply this permission to specific partners or to any partner.
From the Contract step, click to update the terms and conditions (if desired) and then select the file for the updated terms and conditions. When finished, click .
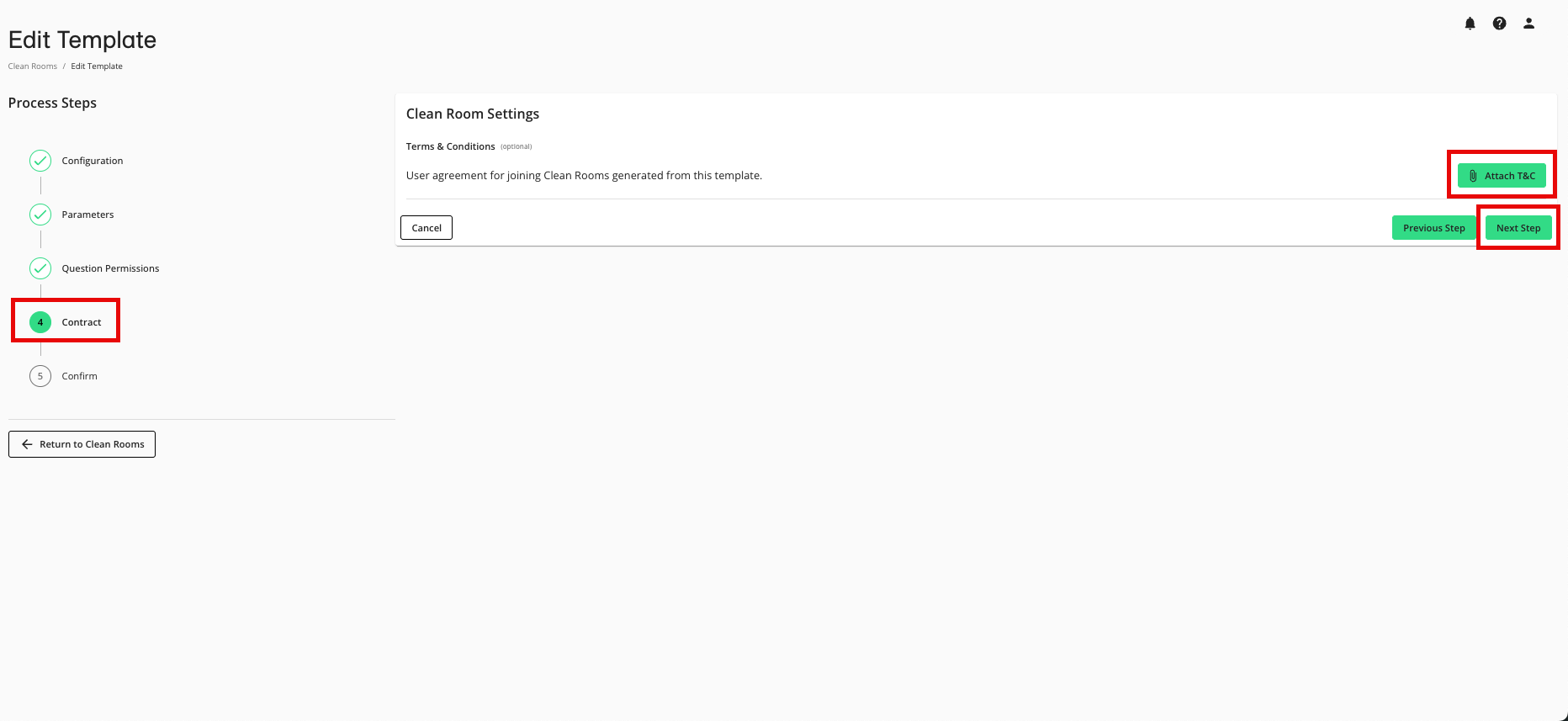
Note
This is most commonly used for test and evaluation clean rooms, which do not require full contracting with LiveRamp or the clean room owner.
The terms and conditions must be in PDF format.
For more information on terms and conditions, see "Attaching Terms and Conditions to Clean Room Templates".
From the Confirm step, review the edits and then click to save the edits to the template.
Provision Your Datasets to the Clean Room Template
After your data connections have been successfully connected, you can provision each associated dataset to the Media Intelligence clean room template so it’s available to assign to questions.
During provisioning, you can configure the dataset so that only certain fields or field values are queryable. You can also rename fields (to make them easier to map when assigning the dataset to questions) and create new fields by applying a transformation to an existing field or fields.
Note
At this step, be sure to only create filters that will apply to all brands you’ll work with. When you generate a clean room for a specific brand from this template, you can then edit the dataset configuration to filter the data further so that the brand only sees data that applies to them.
For complete instructions, see “Provision a Dataset to a Clean Room".
Assign Your Datasets to Questions in the Template
After you’ve provisioned your datasets to the Media Intelligence clean room template, you can then assign those datasets to the template’s questions.
This involves the following steps:
Assigning the dataset owner to each dataset used in that question.
Assigning the appropriate dataset to each dataset macro for that question.
Assigning the appropriate field to each field macro for that question.
This makes sure that each macro in the question is being linked to the correct field or dataset.
Note
You need to assign your datasets to the questions in each Media Intelligence clean room.
The question names start with a number and category to make it easier to reference them.
All questions use your CID | RampID mapping dataset. Some questions use your publisher audience dataset and some questions use your exposures dataset.
For instructions on how to assign datasets for each question type, see the sections below (for complete instructions on assigning datasets to questions, see “Configure Datasets for Questions”).
Note
If the field from your dataset does not appear in the dropdown menu when assigning fields to field macros, it is most likely because the data type for that field in the dataset is not the same as the data type that the field macro expects.
For example, if your dataset was connected with the CID field set as a “Long” data type, it will not show up in the Assign Dataset Fields step because the macro is looking for a “String” value to map to. You can use one of the following methods to resolve this:
Change the field to use the appropriate field type in the dataset in your cloud environment
If you’re not able to adjust the data at source, a new field can be added to the provisioned dataset from within the clean room, cast as the correct data type to align with the field macro. Note that the new field must have a different name than the original field. Also note that this might add to the processing time when questions are run.
See below for an example of the creation of a new field to change the data type from "LONG" to "TIMESTAMP":
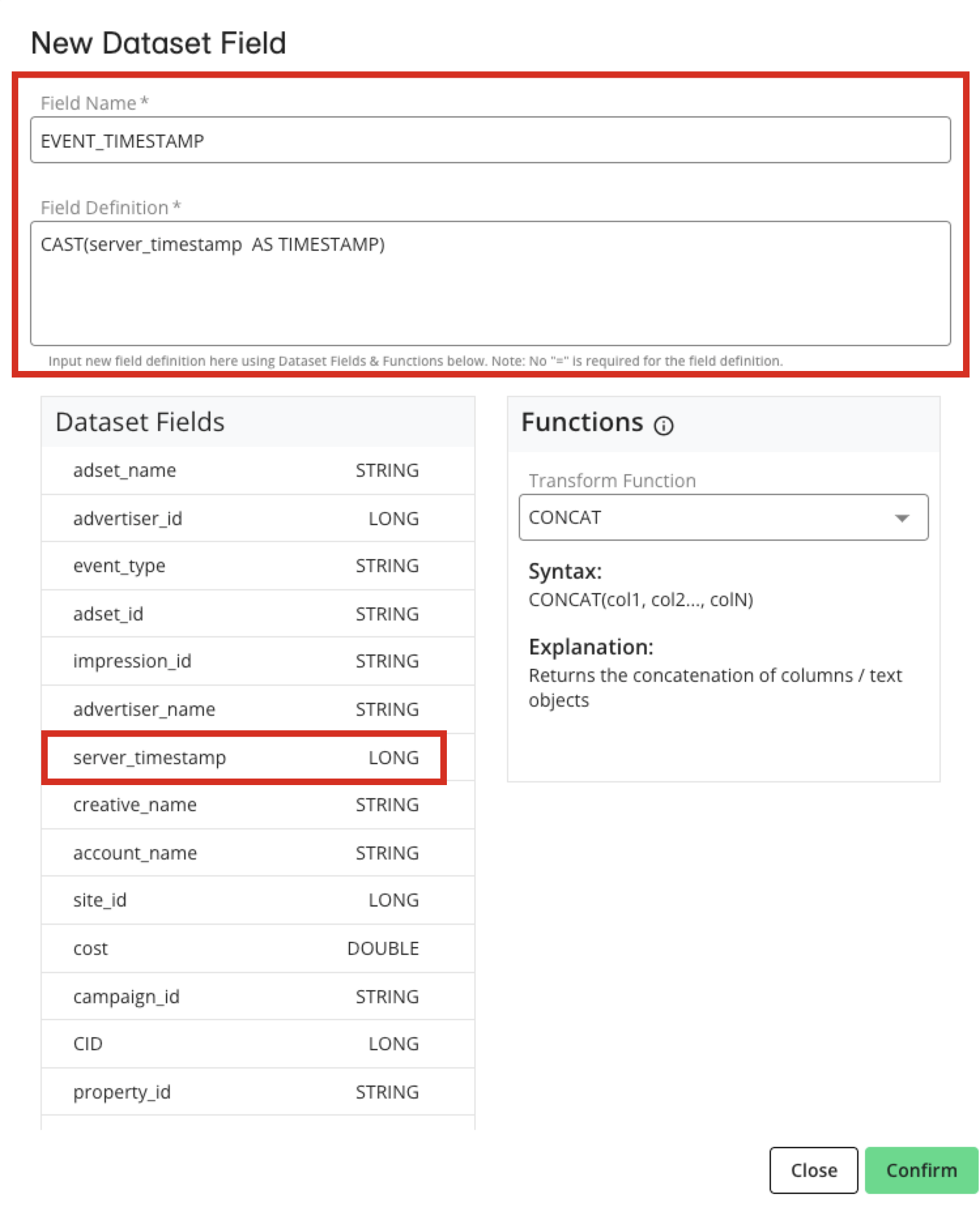
Assign Datasets for Questions That Utilize Only Your CID | RampID Mapping Dataset
Perform the steps below for the following question that utilizes your CID | RampID mapping dataset:
9. Overlap Analysis: What is the overlap between Advertiser CRM and publisher universe?
To assign datasets for this question:
From the navigation menu, select Clean Room → Clean Rooms to open the Clean Rooms page.
Select the Templates tab.

From the More Actions menu (three dots) for the Media Intelligence template, select Edit.

From the clean room menu, select Questions and then click next to the question.
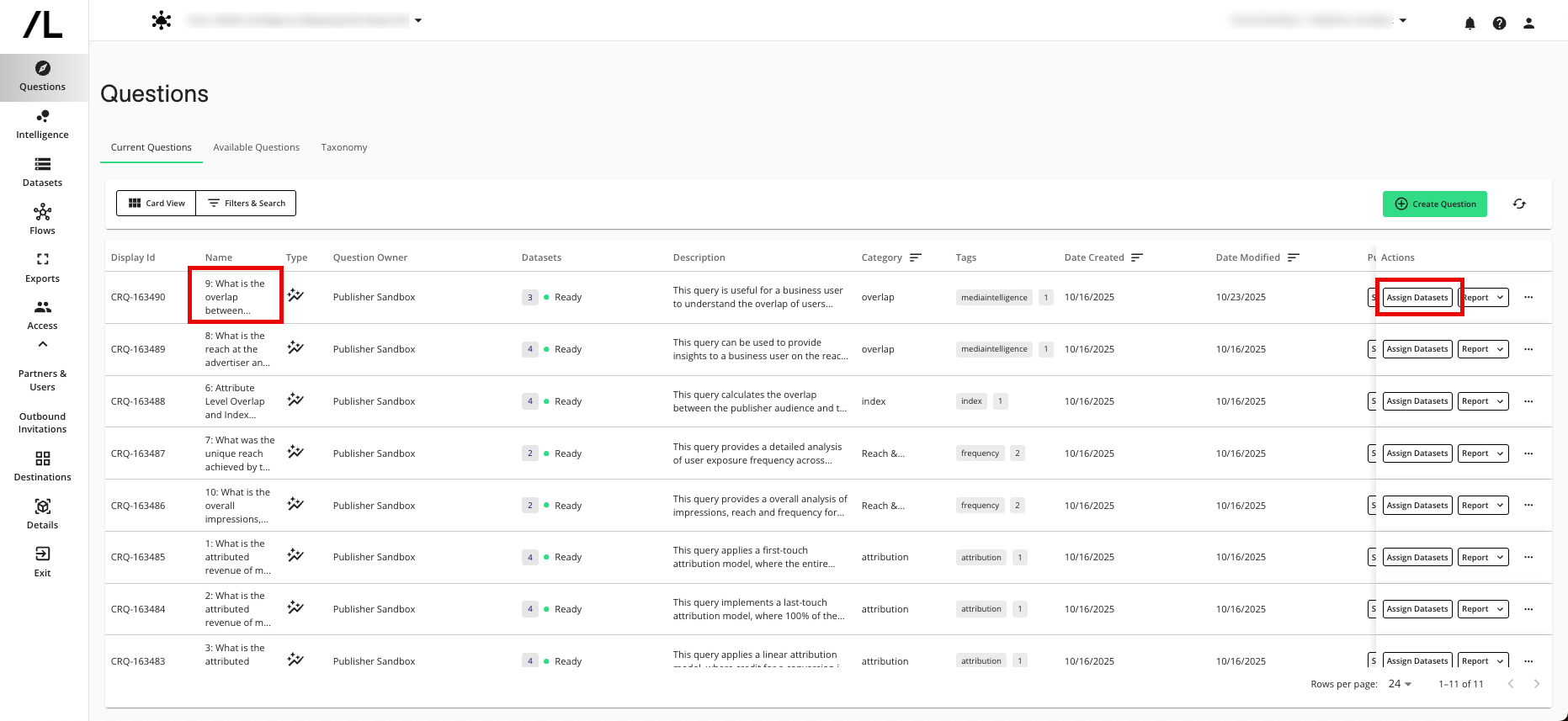
The Manage Datasets wizard displays the dataset macros that are enabled for the question. For information about dataset macros, see "Add a Macro for a Dataset Type".
Assign your organization as the owner for the “pubmap” dataset and then click .
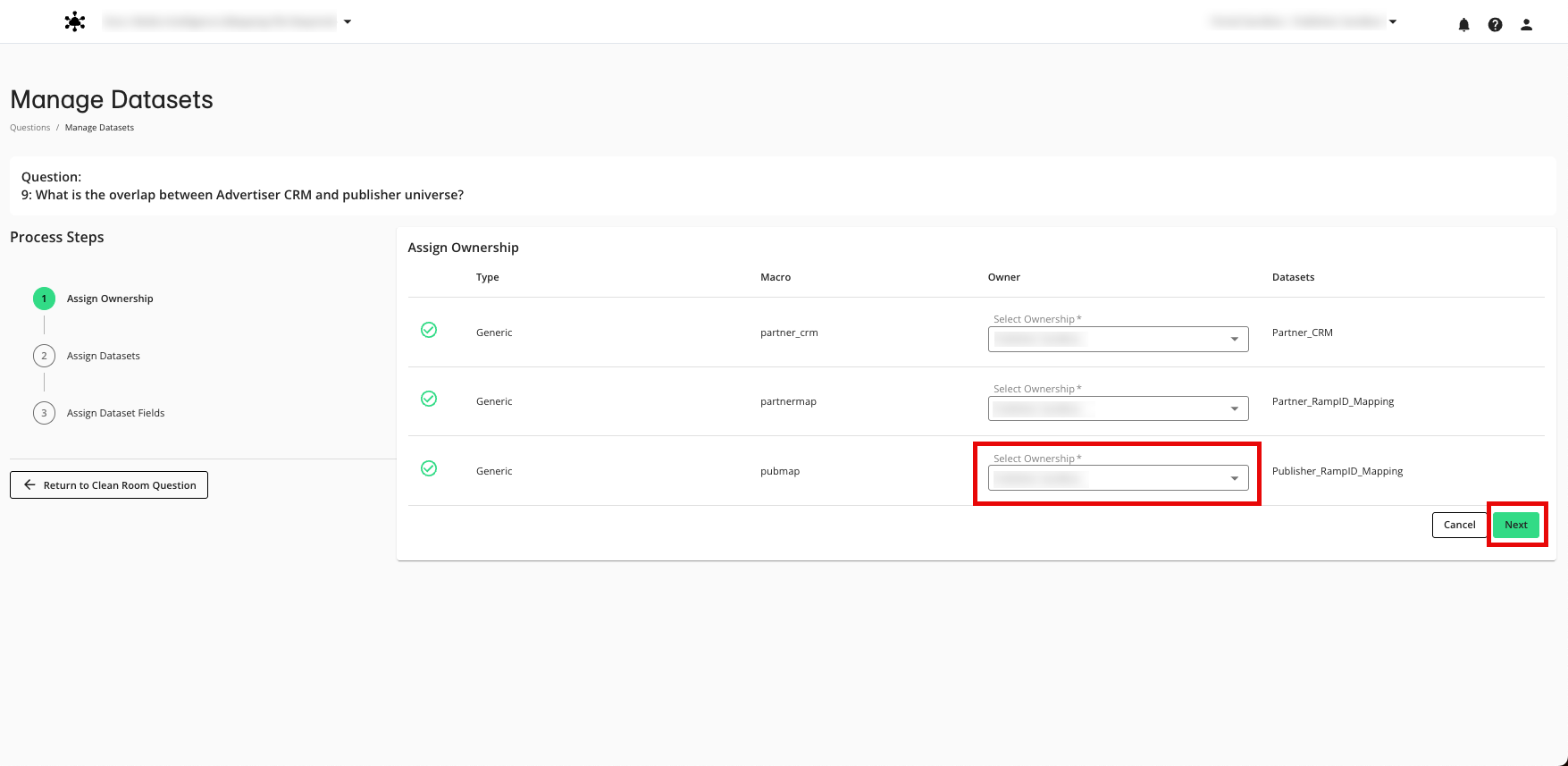
Use the table below to assign the datasets to the appropriate dataset macro.
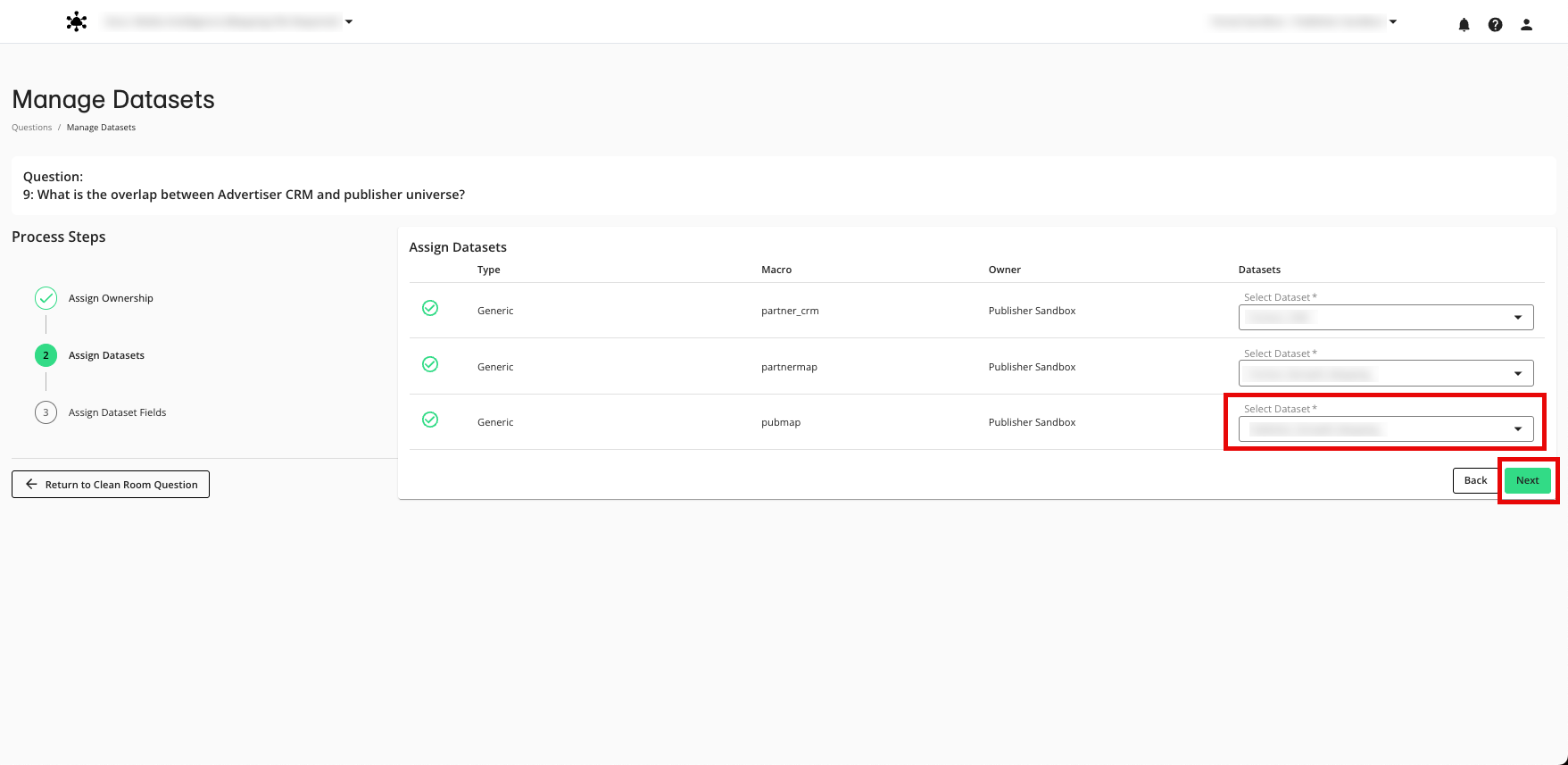
Use the table below to assign the fields to the appropriate field macro.
Dataset Macro Name | Publisher Dataset Used | Field Macro Name | Publisher Field to Assign |
|---|---|---|---|
@pubmap | CID | RampID mapping | @cid (string) | Your CID field |
@rampid (string) | Your RampID field |
Assign Datasets for Questions That Utilize Your Publisher Audience Dataset
Perform the steps below for the following question that utilizes your publisher audience dataset:
6. Attribute Overlap Index: Attribute Level Overlap and Index Report
To assign datasets for this question:
From the navigation menu, select Clean Room → Clean Rooms to open the Clean Rooms page.
Select the Templates tab.

From the More Actions menu (three dots) for the Media Intelligence template, select Edit.

From the clean room menu, select Questions and then click next to the question.
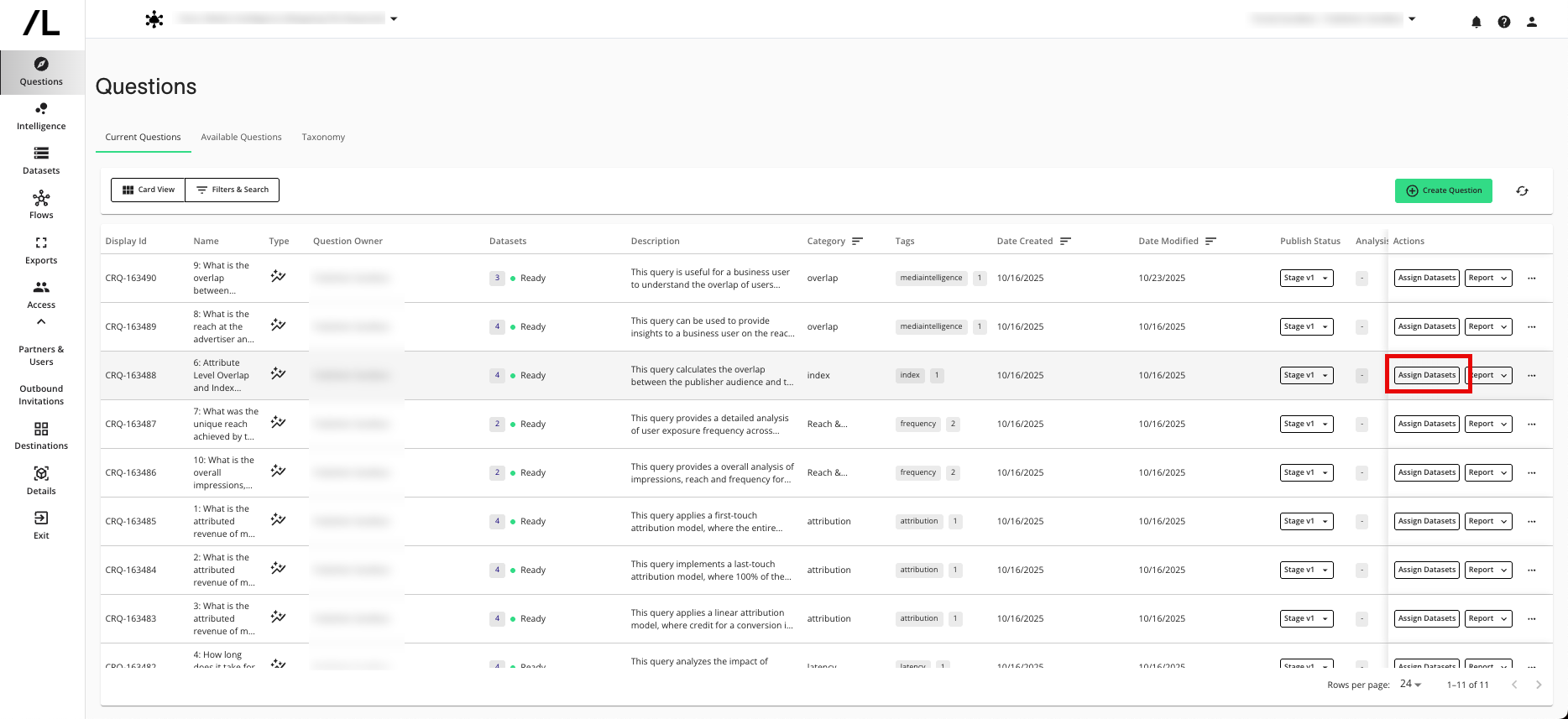
The Manage Datasets wizard displays the dataset macros that are enabled for the question. For information about dataset macros, see "Add a Macro for a Dataset Type".
Assign your organization as the owner for the “publisher_audience” and “pubmap” datasets.
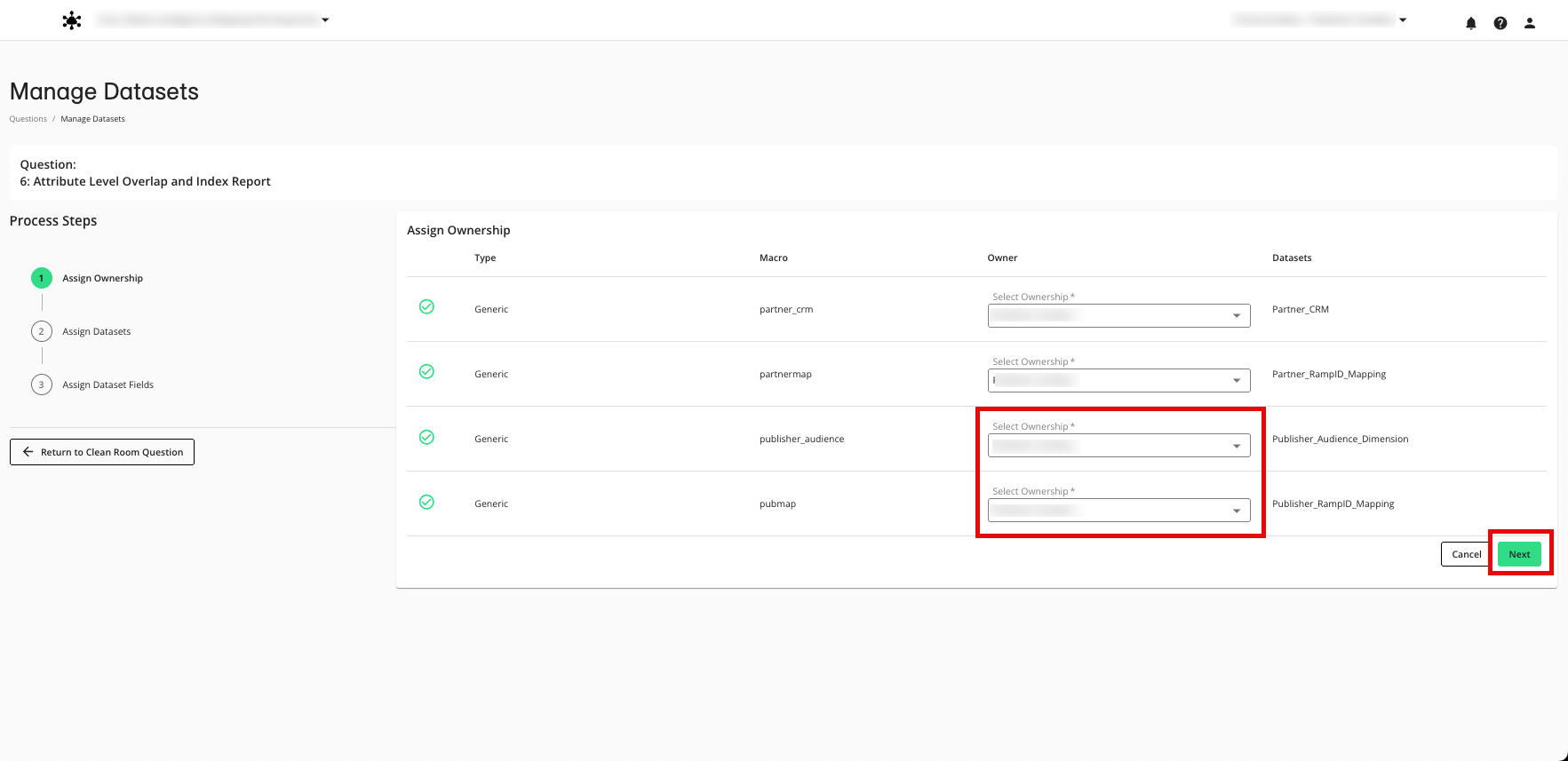
Use the table below to assign the datasets to the appropriate dataset macro.
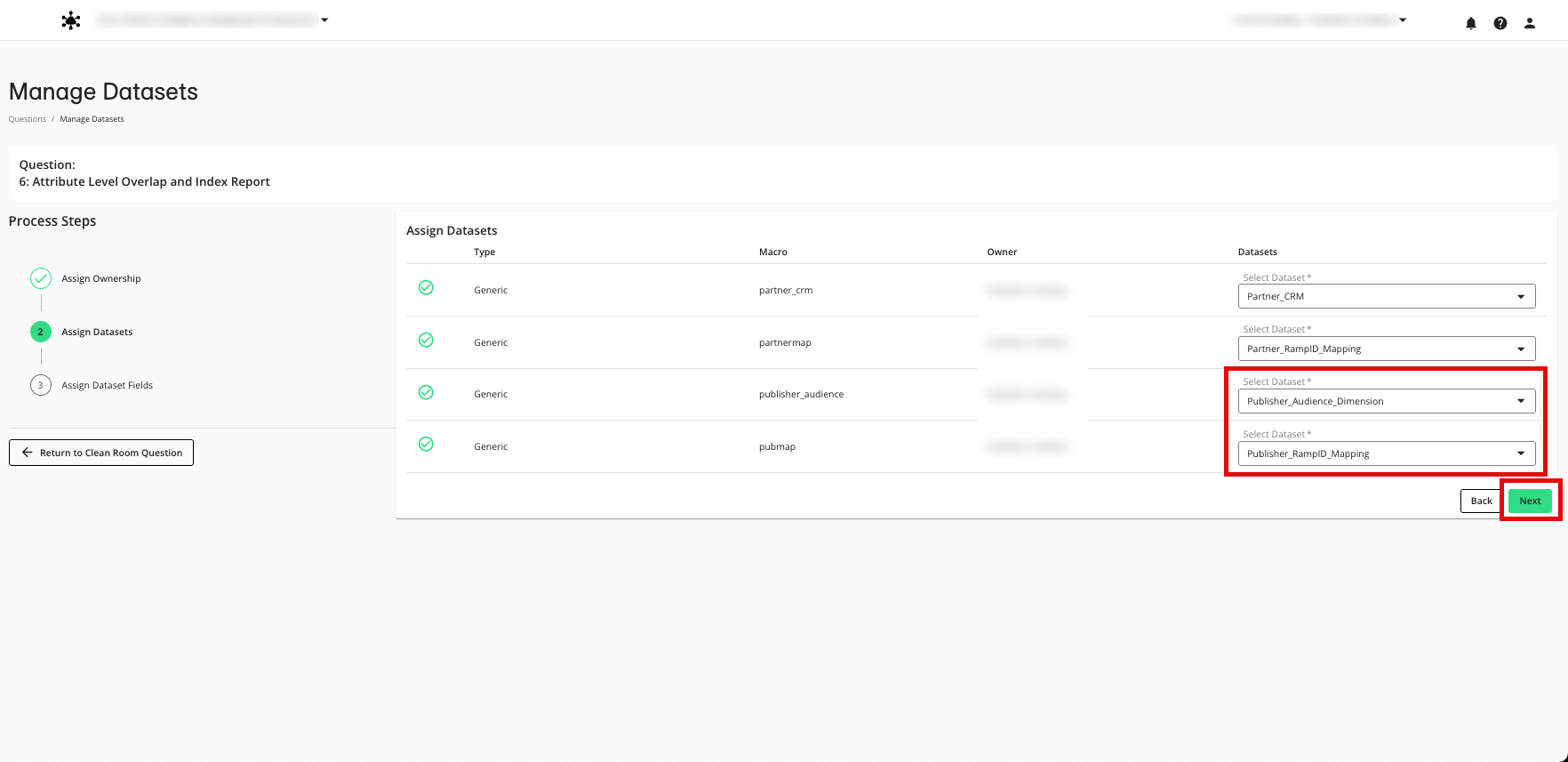
Use the table below to assign the fields to the appropriate field macro.
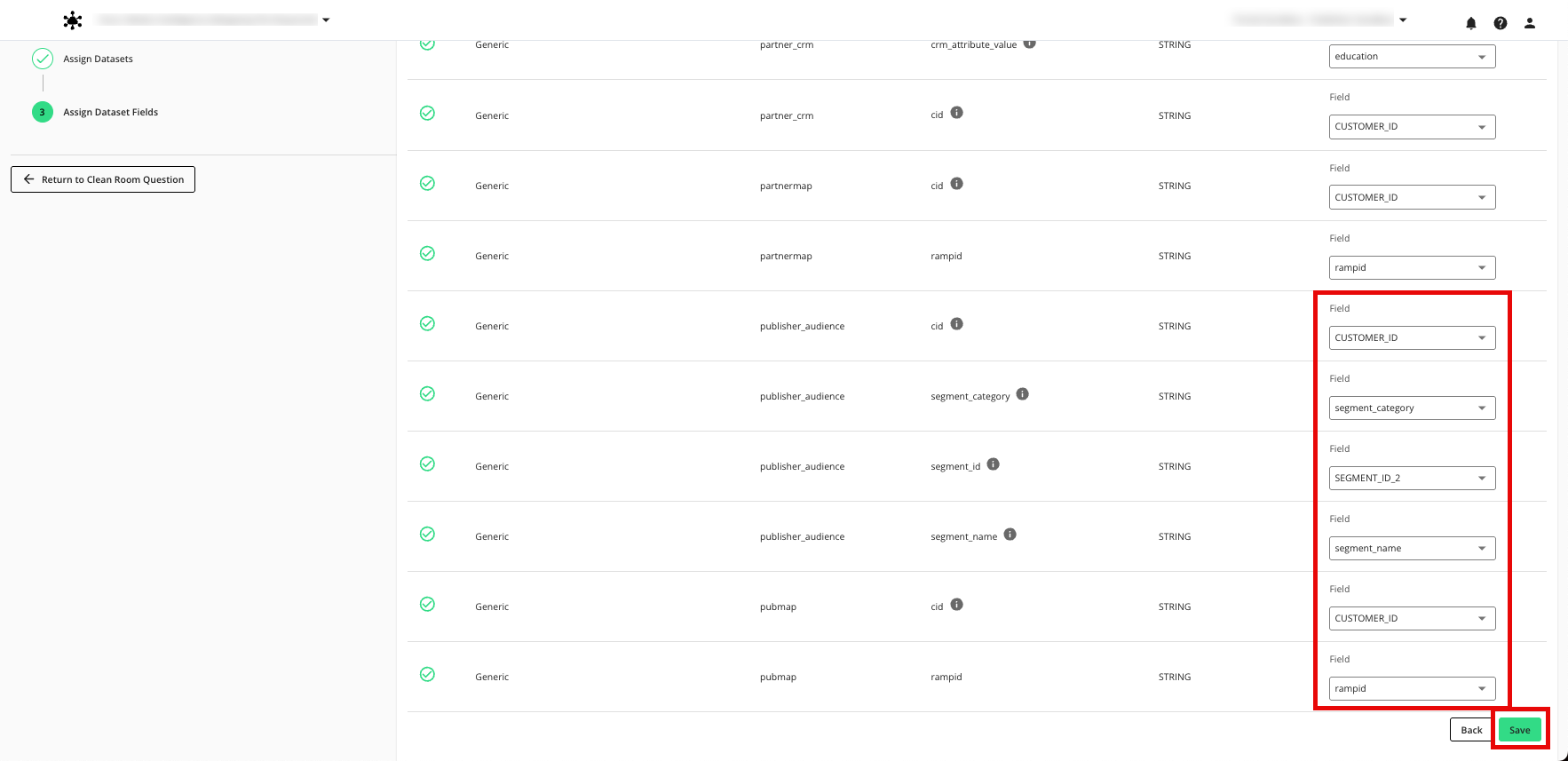
Dataset Macro Name | Publisher Dataset Used | Field Macro Name | Publisher Field to Assign |
|---|---|---|---|
@pubmap | CID | RampID mapping | @cid (string) | Your CID field |
@rampid (string) | Your RampID field | ||
@publisher_audience | Publisher audience | @cid (string) | Your CID field |
@segment_id | Your audience segment ID field | ||
@segment_category | Your segment category field | ||
@segment_name | Your segment name field |
Assign Datasets for Questions That Utilize Your Exposures Dataset
Perform the steps below for the following questions that utilize your exposures dataset:
1. First Touch Attribution: What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on first touch with the custom attribution window?
2. Last Touch Attribution: What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on last touch with the custom attribution window?
3. Linear Attribution: What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on linear attribution with custom attribution window?
4. Latency Analysis: How long does it take for a user to convert after first touch and last touch?
5. Frequency Analysis: What is the optimal frequency to deliver my campaigns?
7. Reach Analysis: What was the unique reach achieved by the advertiser and at what frequency was the media served?
8. Reach Analysis: What is the reach at the advertiser and campaign level and what is the overlap percentage with CRM?
10. Reach And Frequency: What are the overall impressions, reach and frequency achieved across all advertisers and brands?
To assign datasets for these questions:
From the navigation menu, select Clean Room → Clean Rooms to open the Clean Rooms page.
Select the Templates tab.

From the More Actions menu (three dots) for the Media Intelligence template, select Edit.

From the Clean Room menu, select Questions and then click next to the desired question.
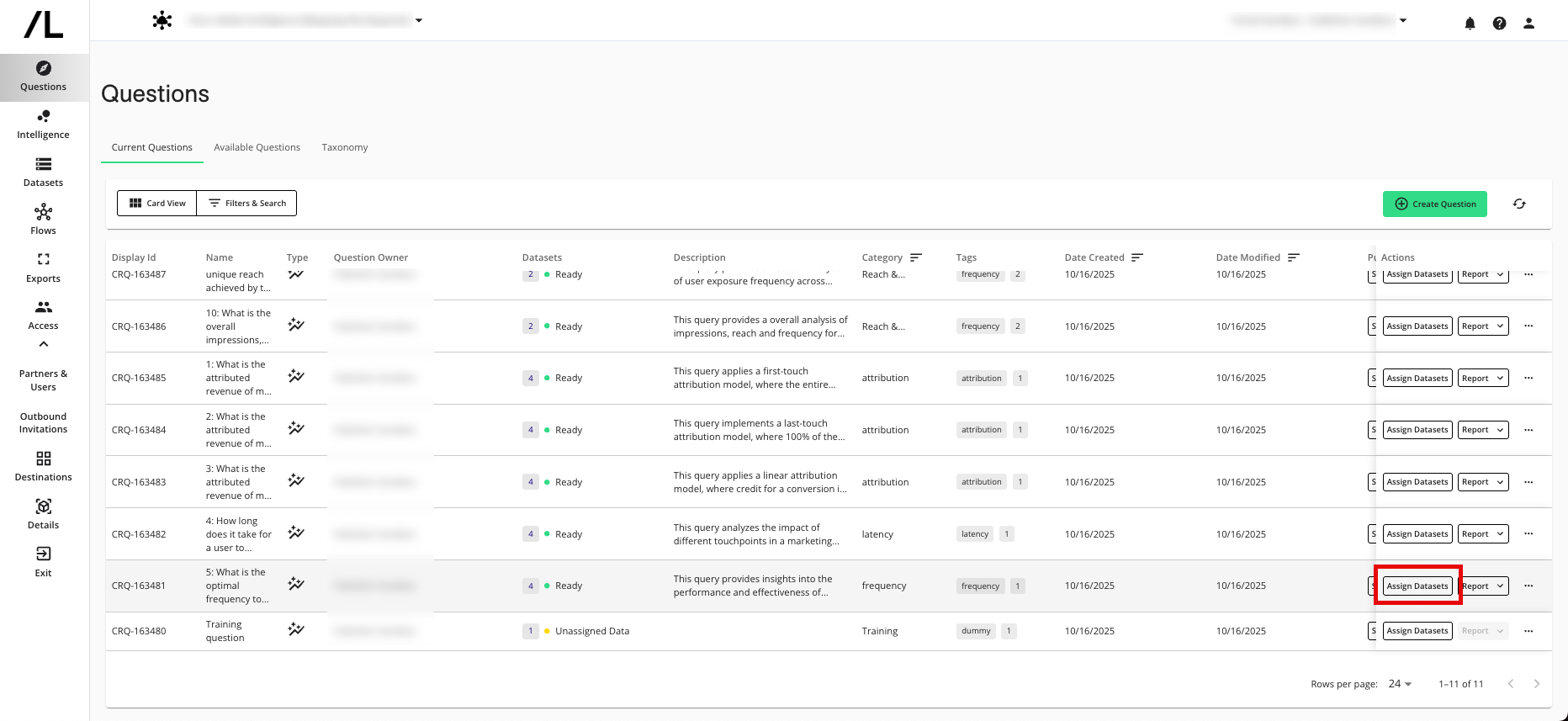
The Manage Datasets wizard displays the dataset macros that are enabled for the question. For information about dataset macros, see "Add a Macro for a Dataset Type".
Assign your organization as the owner for the “exposures” and “pubmap” datasets.
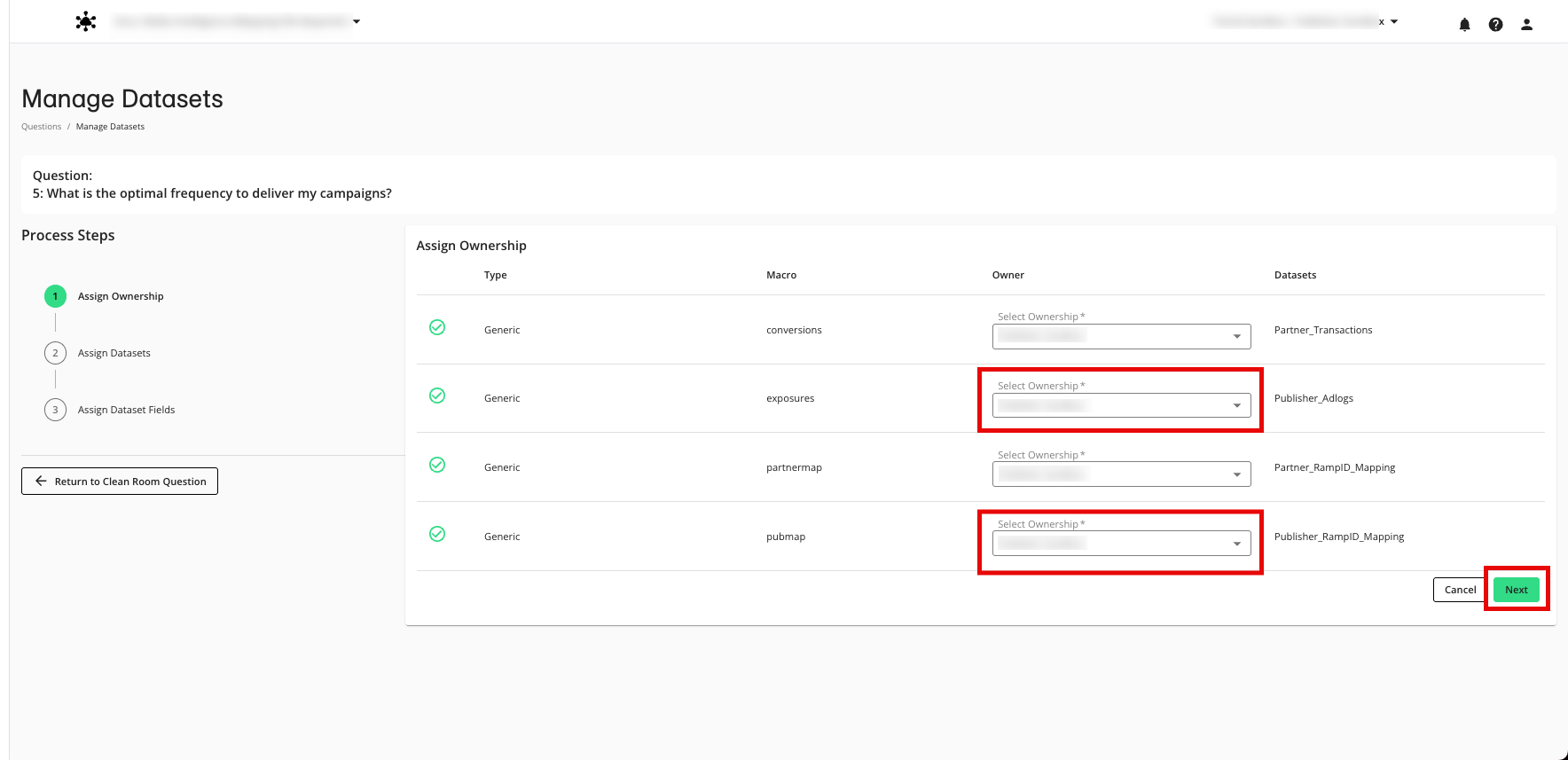
Use the table below to assign the datasets to the appropriate dataset macro.
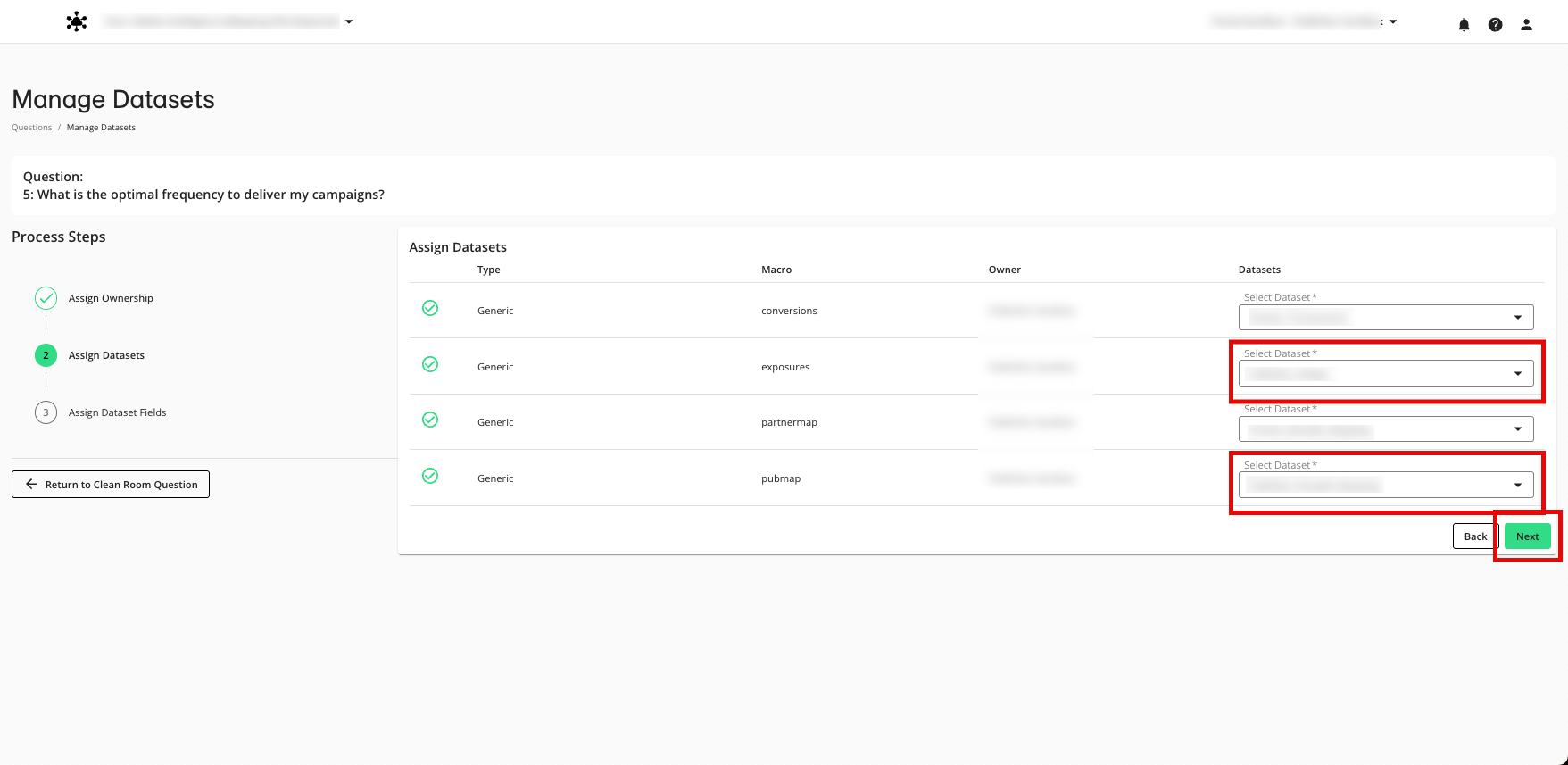
Use the table below to assign the fields to the appropriate field macro.
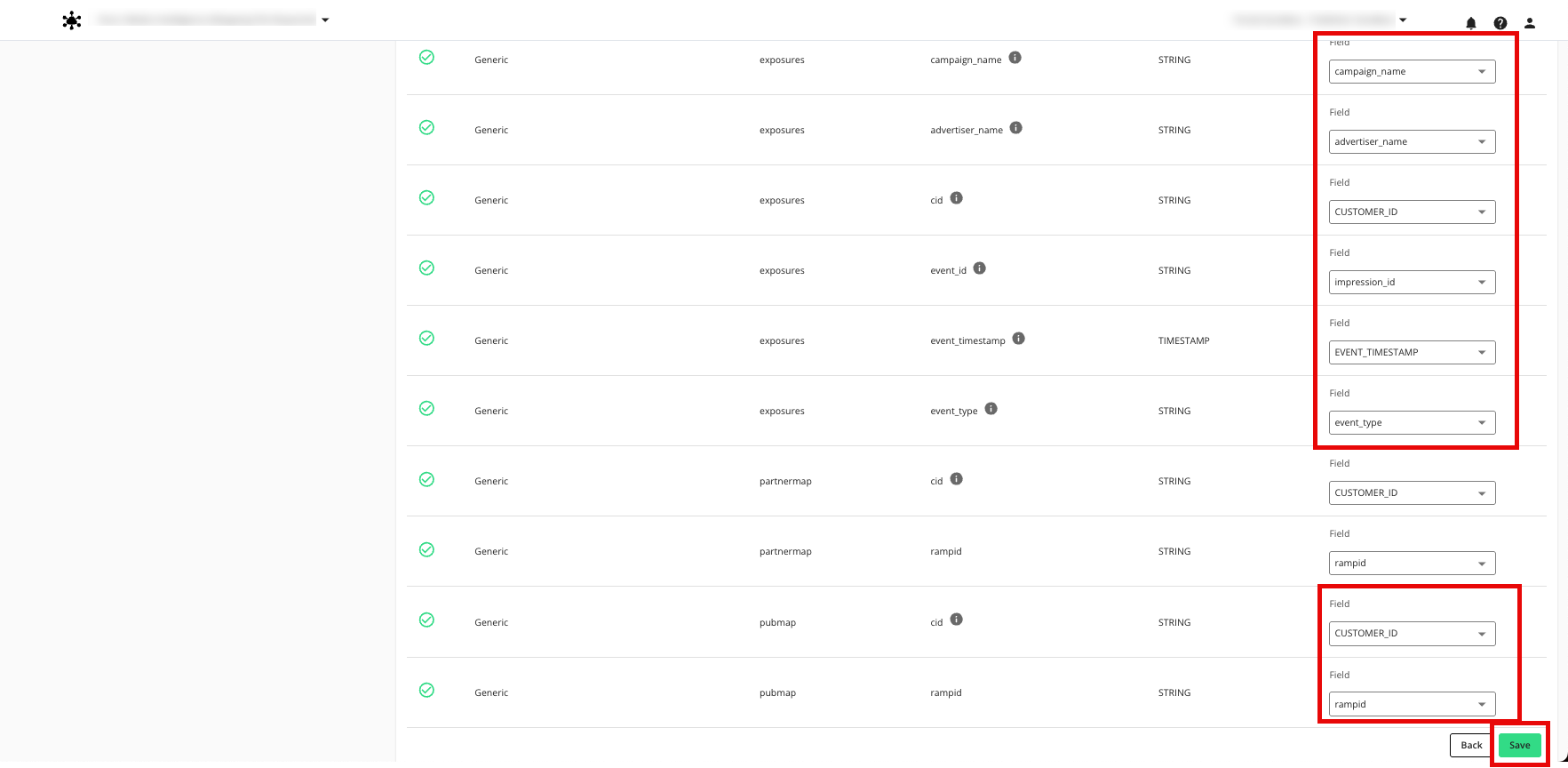
Dataset Macro Name | Publisher Dataset Used | Field Macro Name | Publisher Field to Assign |
|---|---|---|---|
@pubmap | CID | RampID mapping | @cid (string) | Your CID field |
@rampid (string) | Your RampID field | ||
@exposures | Exposures | @cid (string) | Your CID field |
@advertiser_name | Your advertiser name field | ||
@campaign_name | Your campaign name field |
Generate a Clean Room for the Brand
Once you’ve finished configuring the Media Intelligence template, you can then generate a clean room for a specific brand. During clean room generation, you can also customize the clean room for the specific brand in the following areas, if needed:
Configuration:
Clean room name
Description
End date
Cloud and region
Parameters
Question Permissions
Note
Do not make any changes to the Questions Included or the Intelligence tabs.
For detailed instructions on generating a clean room for a brand, see “Generate a New Clean Room From a Template”.
Filter the Exposures Dataset for the Brand
Before you invite the brand to the clean room, you’ll want to edit the configuration for the exposures datasets to filter the values so that the brand only sees data that is relevant to them:
Enter the desired clean room.
From the clean room navigation menu, select Datasets (if necessary).
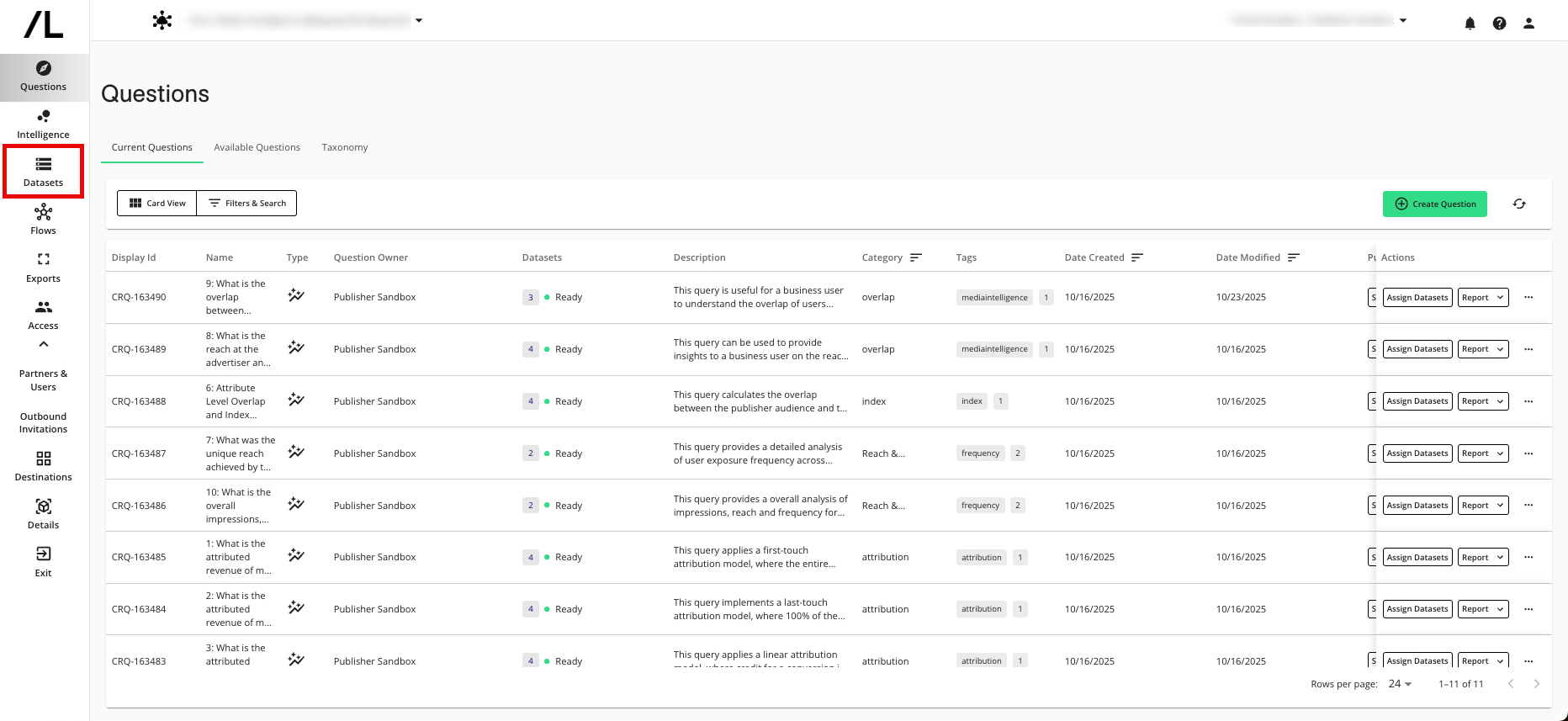
In the row for the exposures dataset, click the More Actions menu (the three dots) and then select Edit Configuration.
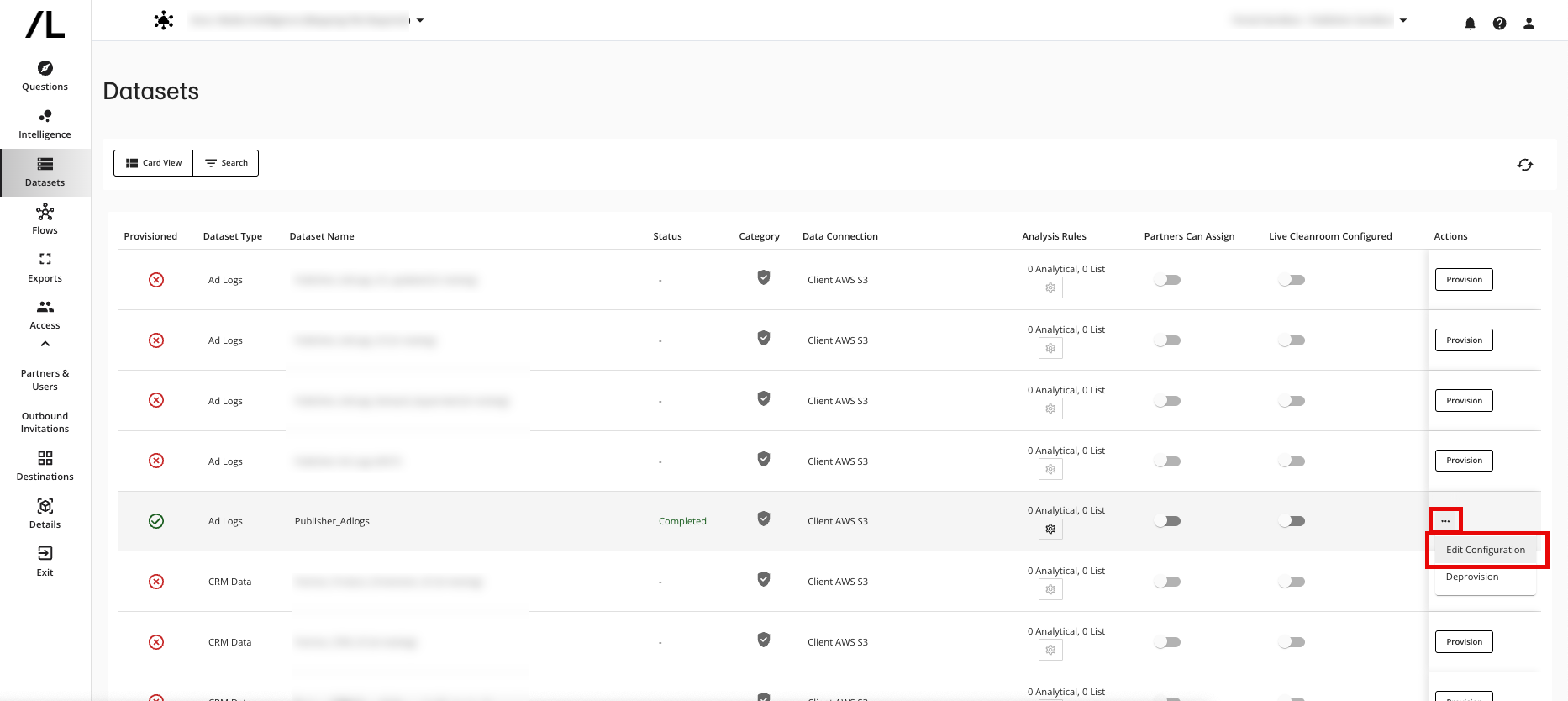
In the row for the field advertiser_name, select the “Equals” operator and then enter the brand name in the “Filter Value(s)” field.
Click .
Invite the Brand to the Clean Room
Once you’ve generated a clean room for a brand and edited its configuration, you can then invite the brand partner to join the clean room:
From your clean room, select Access → Partners & Users.
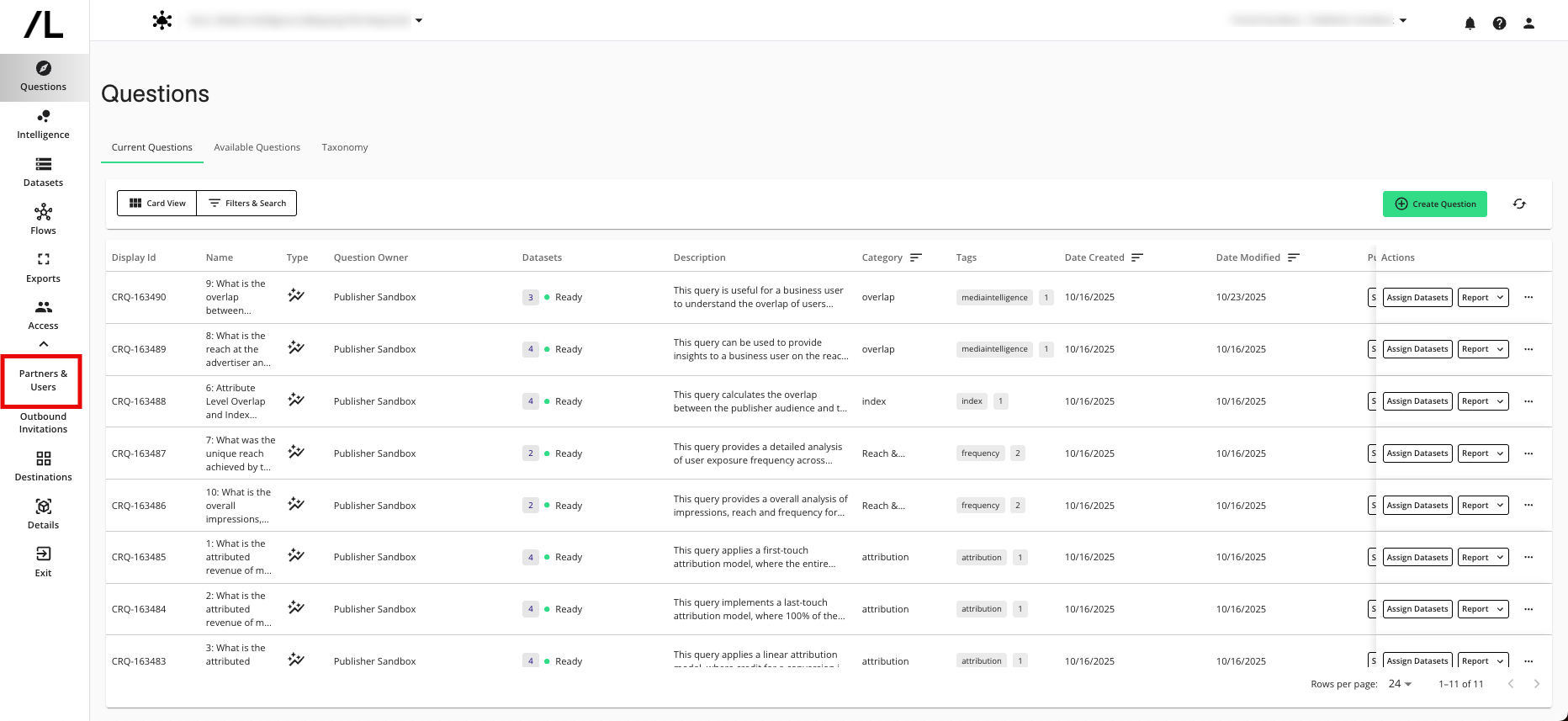
Click .
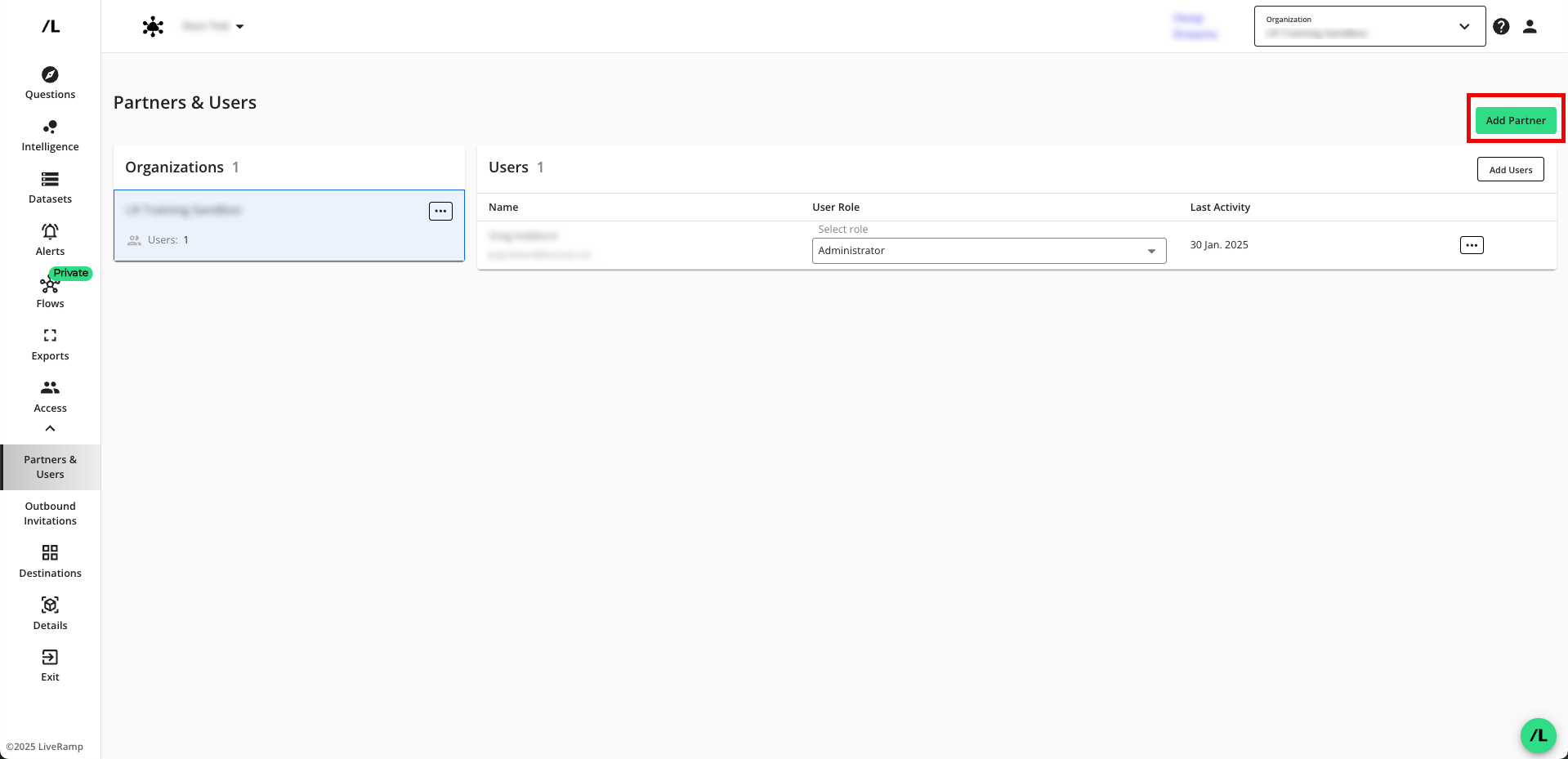
Enter the email address where your partner wants you to send the clean room invitation and accept or modify the invitation message body, and then click .
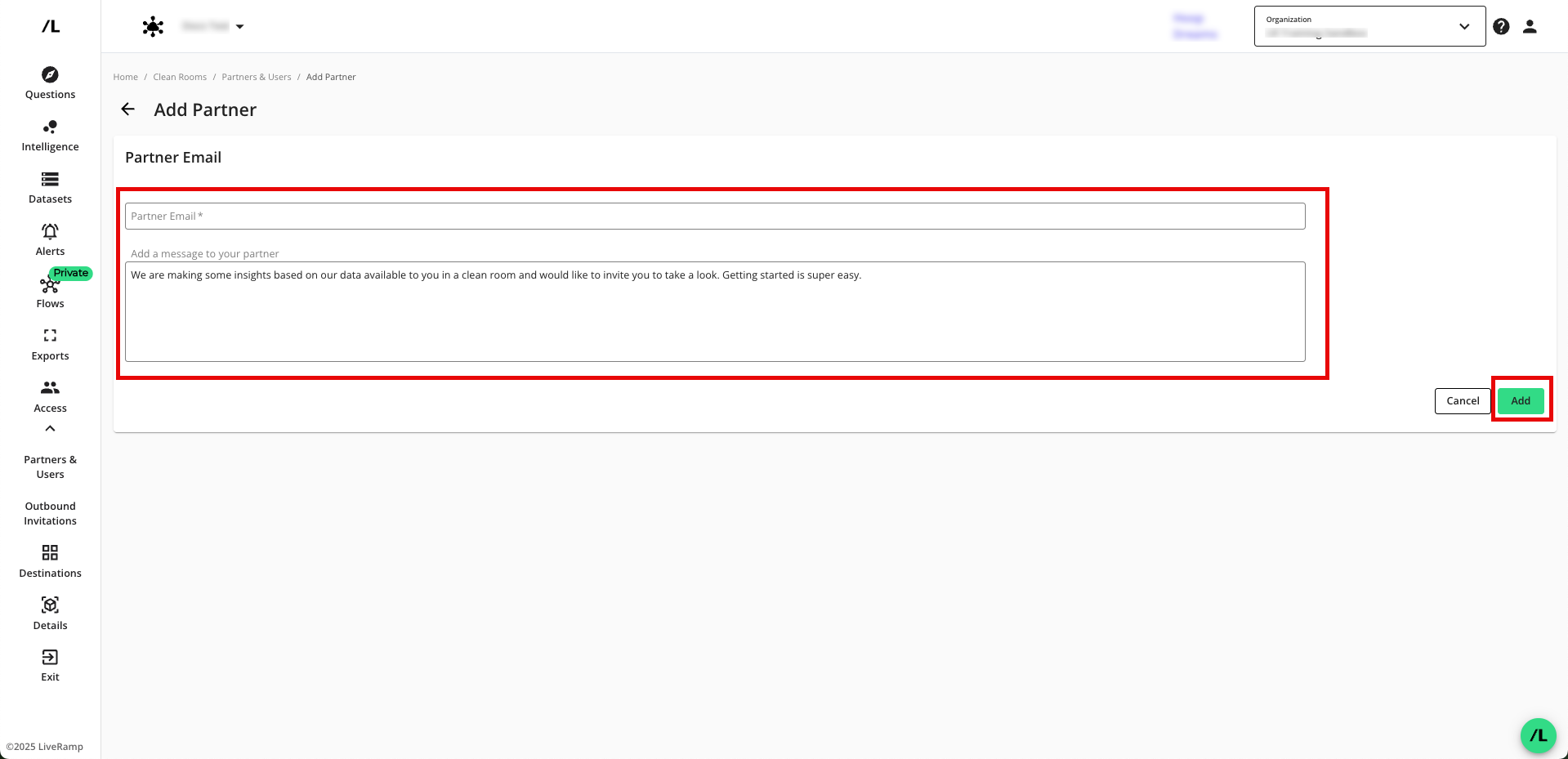
From the confirmation dialog that appears, click .

The partner will receive an email invitation from no-reply@email.habu.com that includes a link to click to open the Clean Room Inbound Invitations page, where they can accept the invitation.
Note
If the partner does not have an active LiveRamp Clean Room account, there might be a delay between when the partner accepts the invitation and when collaboration is enabled in the UI (until an account is created for the partner by LiveRamp).
The partner can now navigate to Clean Room → Clean Rooms from the navigation menu to access the clean room.
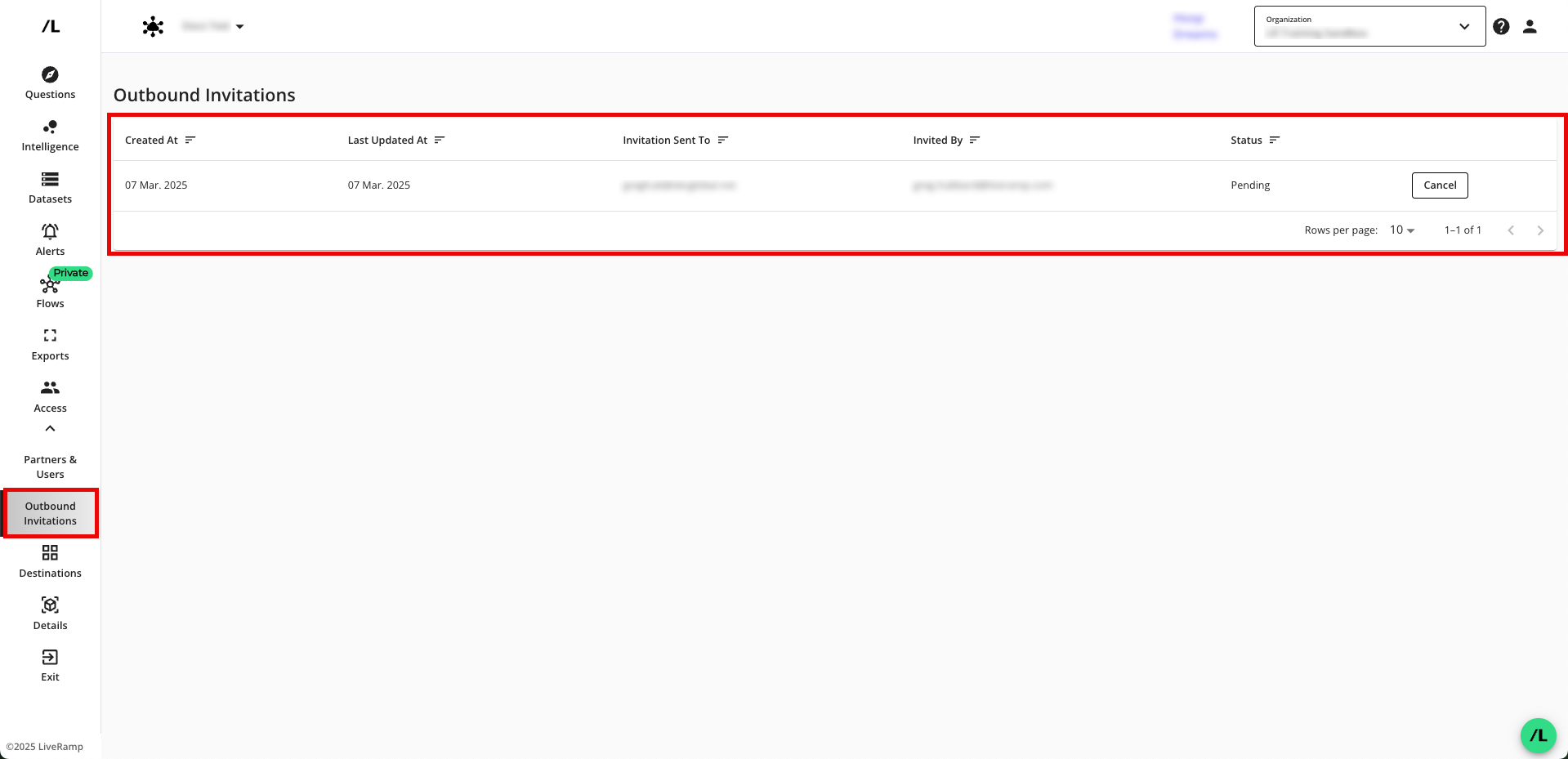
Note
On the Outbound Invitations page, you can view all the invitations you've sent and their statuses.
Run Reports
Once the brand has performed their necessary actions (accepted the clean room invitation, connected their data, provisioned their datasets to the clean room, and assigned their datasets to the questions), reports can then be run.
Depending on your arrangement with the brand, either you or the brand will run questions and schedule question runs to generate reports. If the brand is handling this step, skip this section.
Where applicable, questions will have Runtime Parameters (RTPs) and/or data partition options at runtime. RTPs can be used to modify select inputs for a particular query without having to modify SQL. They enable flexibility for the end-user to adjust their analysis needs. For example, the ability to choose specific windows of time can significantly influence an analysis output.
See the sections below for information on each question, and its runtime and partition parameters.
9. Overlap Analysis: What is the overlap between Advertiser CRM and publisher universe?
This query is useful for a business user to understand the overlap of users between you and the publisher, which can help with targeting and advertising strategies.
Runtime parameters: None
Partition parameters: None
-- What is the overlap between Advertiser CRM and publisher universe? SELECT 'Advertiser and Publisher Overalp' as Dimension ,count(distinct @pubmap.@cid) as Overlap_Count from @partner_crm INNER JOIN @partnermap on @partner_crm.@cid = @partnermap.@cid INNER JOIN @pubmap on @pubmap.@rampid = @partnermap.@rampid where @partner_crm.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'
6. Attribute Overlap Index: Attribute Level Overlap and Index Report
This query calculates the overlap between the publisher audience and the partner CRM data sets & indexes advertiser CRM attributes against publisher user segments.
Runtime parameters: Attribute field specified when the dataset was assigned to the question, such as “crm_attribute” (highlighted in SQL)
Partition parameters: None
-- Attribute level overlap and index report SELECT X1.ATTRIBUTE AS ATTRIBUTE, X1.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE AS ATTRIBUTE_VALUE, X1.segment_category AS AUDIENCE_SEGMENT_CATEGORY, X1.segment_id AS segment_id, X1.segment_name AS AUDIENCE_SEGMENT_NAME, X1.OVERLAP AS OVERLAP, X2.SEGMENT_SIZE AS AUDIENCE_SEGMENT_SIZE, X3.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SIZE AS ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SIZE, X4.DENOM_TOTAL AS TOTAL_SIZE, ROUND(TRY_DIVIDE(TRY_DIVIDE(1.0*X1.OVERLAP, 1.0*X3.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SIZE), TRY_DIVIDE(1.0*X2.SEGMENT_SIZE, 1.0*X4.DENOM_TOTAL)), 2) AS ATTRIBUTE_AUDIENCE_INDEX FROM ( SELECT '@CRM_ATTRIBUTE' AS ATTRIBUTE, @partner_crm.@crm_attribute_value AS ATTRIBUTE_VALUE, --'EDUCATION' AS ATTRIBUTE, --@partner_crm.@education AS ATTRIBUTE_VALUE, @publisher_audience.@segment_id AS segment_id, @publisher_audience.@segment_category AS segment_category, @publisher_audience.@segment_name AS segment_name, COUNT(DISTINCT @partner_crm.@cid) AS OVERLAP FROM @partner_crm INNER JOIN @partnermap on @partner_crm.@cid = @partnermap.@cid INNER JOIN @pubmap on @partnermap.@rampid = @pubmap.@rampid INNER JOIN @publisher_audience on @publisher_audience.@cid = @pubmap.@cid where @partner_crm.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED' GROUP BY 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ) X1, ( SELECT @publisher_audience.@segment_id AS segment_id, @publisher_audience.@segment_category AS segment_category, @publisher_audience.@segment_name AS segment_name, COUNT(DISTINCT @publisher_audience.@cid) AS SEGMENT_SIZE FROM @publisher_audience INNER JOIN @pubmap on @publisher_audience.@cid = @pubmap.@cid where @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED' GROUP BY 1,2,3 ) X2, ( SELECT '@CRM_ATTRIBUTE' AS ATTRIBUTE, @partner_crm.@crm_attribute_value AS ATTRIBUTE_VALUE, COUNT(DISTINCT @partner_crm.@cid) AS ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SIZE FROM @partner_crm inner join @partnermap on @partner_crm.@cid = @partnermap.@cid where @partner_crm.@cid IS NOT NULL and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @partnermap.@rampid is not null and @partnermap.@rampid != '0' and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED' GROUP BY 1, 2 ) X3, ( SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT @pubmap.@cid) AS DENOM_TOTAL FROM @pubmap where @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED' ) X4 WHERE X1.ATTRIBUTE = X3.ATTRIBUTE AND X1.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE = X3.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE AND X1.SEGMENT_CATEGORY = X2.SEGMENT_CATEGORY AND X1.SEGMENT_NAME = X2.SEGMENT_NAME AND X1.SEGMENT_ID = X2.SEGMENT_ID
10. Reach And Frequency: What are the overall impressions, reach and frequency achieved across all advertisers and brands?
This query provides an overall analysis of impressions, reach and frequency for the total brand, by counting unique customer identifiers (CIDs) and RampIDs that were served varying numbers of impressions.
Runtime parameters: None
Partition parameters: Exposure Start and End Dates
with user_lvl_freq_cid AS ( SELECT @exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name ,@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name ,@exposures.@cid as cid ,count(distinct @exposures.@event_id) as impressions_served FROM @exposures inner join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid where @exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED' group by 1,2,3 ), user_lvl_freq_rampid AS ( SELECT @exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name ,@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name ,@pubmap.@rampid as rmn_rampid ,count(distinct @exposures.@event_id) as impressions_served FROM @exposures inner join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid where @exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED' group by 1,2,3 ), combined_dataset as ( SELECT 'campaign level' as metric_level ,'count of cid' as frequency_type ,advertiser_name ,campaign_name ,sum(impressions_served) as impressions_served ,count(DISTINCT cid) as targeted_customers from user_lvl_freq_cid group by 3,4 union all SELECT 'campaign level' as metric_level ,'count of rampid' as frequency_type ,advertiser_name ,campaign_name ,sum(impressions_served) as impressions_served ,count(DISTINCT rmn_rampid) as targeted_customers from user_lvl_freq_rampid group by 3,4 union all SELECT 'advertiser level' as metric_level ,'count of cid' as frequency_type ,advertiser_name ,'all campaigns' as campaign_name ,sum(impressions_served) as impressions_served ,count(DISTINCT cid) as targeted_customers from user_lvl_freq_cid group by 3 union all SELECT 'advertiser level' as metric_level ,'count of rampid' as frequency_type ,advertiser_name ,'all campaigns' as campaign_name ,sum(impressions_served) as impressions_served ,count(DISTINCT rmn_rampid) as targeted_customers from user_lvl_freq_rampid group by 3 union all SELECT 'overall' as metric_level ,'count of cid' as frequency_type ,'all advertisers' as advertiser_name ,'all campaigns' as campaign_name ,sum(impressions_served) as impressions_served ,count(DISTINCT cid) as targeted_customers from user_lvl_freq_cid union all SELECT 'overall' as metric_level ,'count of rampid' as frequency_type ,'all advertisers' as advertiser_name ,'all campaigns' as campaign_name ,sum(impressions_served) as impressions_served ,count(DISTINCT rmn_rampid) as targeted_customers from user_lvl_freq_rampid ) select metric_level ,frequency_type ,advertiser_name ,campaign_name ,impressions_served ,targeted_customers from combined_dataset
8. Reach Analysis: What is the reach at the advertiser and campaign level and what is the overlap percentage with CRM?
This query can be used to provide insights on the reach of your advertising campaigns and how many of those users are already in your CRM system. This information can help you make informed decisions about your advertising strategies and target your campaigns more effectively.
Runtime parameters: Attribute field specified when the dataset was assigned to the question, such as “crm_attribute” (highlighted in SQL)
Partition parameters: Exposure Start and End Dates
-- What is the reach at advertiser and campaign level and what is the overlap percentage with CRM?
with campaign as
(
SELECT
advertiser_name
,campaign_name
,count(DISTINCT pub.cid) as users_served_impressions
,count(DISTINCT part.cid) as overlap_with_adv_crm
,COUNT(DISTINCT pub.cid) - COUNT(DISTINCT part.cid) as users_not_known_to_adv
FROM
(select distinct @exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name
, @exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name
, @exposures.@cid as cid
, @pubmap.@rampid as rampid
from @exposures
INNER JOIN @pubmap
on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid) pub
LEFT JOIN
(select distinct @partnermap.@cid as cid
, @partnermap.@rampid as rampid
from @partnermap
INNER JOIN @partner_crm
on @partnermap.@cid = @partner_crm.@cid) part
on pub.rampid = part.rampid
where
pub.cid IS NOT NULL
and pub.rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and pub.rampid is not null and pub.rampid != '0' and pub.rampid != 'UNMATCHED'
group by 1,2
),
advertiser as
(
SELECT
advertiser_name
,count(DISTINCT pub.cid) as users_served_impressions
,count(DISTINCT part.cid) as overlap_with_adv_crm
,COUNT(DISTINCT pub.cid) - COUNT(DISTINCT part.cid) as users_not_known_to_adv
FROM
(select distinct @exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name
, @exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name
, @exposures.@cid as cid
, @pubmap.@rampid as rampid
from @exposures
INNER JOIN @pubmap
on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid) pub
LEFT JOIN
(select distinct @partnermap.@cid as cid
, @partnermap.@rampid as rampid
from @partnermap
INNER JOIN @partner_crm
on @partnermap.@cid = @partner_crm.@cid) part
on pub.rampid = part.rampid
where
pub.cid IS NOT NULL
and pub.rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and pub.rampid is not null and pub.rampid != '0' and pub.rampid != 'UNMATCHED'
group by 1
),
overall as
(
SELECT
count(DISTINCT pub.cid) as users_served_impressions
,count(DISTINCT part.cid) as overlap_with_adv_crm
,COUNT(DISTINCT pub.cid) - COUNT(DISTINCT part.cid) as users_not_known_to_adv
FROM
(select distinct @exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name
, @exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name
, @exposures.@cid as cid
, @pubmap.@rampid as rampid
from @exposures
INNER JOIN @pubmap
on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid) pub
LEFT JOIN
(select distinct @partnermap.@cid as cid
, @partnermap.@rampid as rampid
from @partnermap
INNER JOIN @partner_crm
on @partnermap.@cid = @partner_crm.@cid) part
on pub.rampid = part.rampid
where
pub.cid IS NOT NULL
and pub.rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and pub.rampid is not null and pub.rampid != '0' and pub.rampid != 'UNMATCHED'
),
combined as
(
select
'campaign level' as metric_level
,advertiser_name
,campaign_name
,users_served_impressions
,overlap_with_adv_crm
,users_not_known_to_adv
from campaign
union all
select
'advertiser level' as metric_level
,advertiser_name
,'all campaigns' as campaign_name
,users_served_impressions
,overlap_with_adv_crm
,users_not_known_to_adv
from advertiser
union all
select
'overall' as metric_level
,'all advertisers' as advertiser_name
,'all campaigns' as campaign_name
,users_served_impressions
,overlap_with_adv_crm
,users_not_known_to_adv
from overall
)
select
metric_level as Granularity
,advertiser_name
,campaign_name
,users_served_impressions as reach
,overlap_with_adv_crm as reach_overlapping_with_crm
,users_not_known_to_adv as reach_not_in_crm
from combined
7. Reach Analysis: What was the unique reach achieved by the advertiser and at what frequency was the media served?
This query provides a detailed analysis of user exposure frequency across different levels—campaign, advertiser, and overall—by counting unique customer identifiers (CIDs) and RampIDs who were served varying numbers of impressions. The results categorize these users into different frequency buckets, enabling you to understand the distribution of ad exposure among targeted customers and identify potential areas for optimizing ad frequency to enhance campaign effectiveness.
Runtime parameters: None
Partition parameters: Exposure Start and End Dates
-- What was the unique reach achieved by the advertiser and at what frequency was the media served?
with user_lvl_freq_cid AS
(
SELECT
@exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name
,@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name
,@exposures.@cid as cid
,count(distinct @exposures.@event_id) as impressions_served
FROM @exposures
inner join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid
where
@exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'
group by 1,2,3
),
user_lvl_freq_rampid AS
(
SELECT
@exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name
,@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name
,@pubmap.@rampid as rmn_rampid
,count(distinct @exposures.@event_id) as impressions_served
FROM @exposures
inner join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid
where
@exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'
group by 1,2,3
),
combined_dataset as
(
SELECT
'campaign level' as metric_level
,'count of cid' as frequency_type
,advertiser_name
,campaign_name
,CASE WHEN impressions_served>10 then '10+'
when impressions_served between 6 and 10 then '06-10'
else concat('0',impressions_served) end as exposure_frequency
,count(DISTINCT cid) as targeted_customers
from user_lvl_freq_cid
group by 3,4,5
union all
SELECT
'campaign level' as metric_level
,'count of rampid' as frequency_type
,advertiser_name
,campaign_name
,CASE WHEN impressions_served>10 then '10+'
when impressions_served between 6 and 10 then '06-10'
else concat('0',impressions_served) end as exposure_frequency
,count(DISTINCT rmn_rampid) as targeted_customers
from user_lvl_freq_rampid
group by 3,4,5
union all
SELECT
'advertiser level' as metric_level
,'count of cid' as frequency_type
,advertiser_name
,'all campaigns' as campaign_name
,CASE WHEN impressions_served>10 then '10+'
when impressions_served between 6 and 10 then '06-10'
else concat('0',impressions_served) end as exposure_frequency
,count(DISTINCT cid) as targeted_customers
from user_lvl_freq_cid
group by 3,5
union all
SELECT
'advertiser level' as metric_level
,'count of rampid' as frequency_type
,advertiser_name
,'all campaigns' as campaign_name
,CASE WHEN impressions_served>10 then '10+'
when impressions_served between 6 and 10 then '06-10'
else concat('0',impressions_served) end as exposure_frequency
,count(DISTINCT rmn_rampid) as targeted_customers
from user_lvl_freq_rampid
group by 3,5
union all
SELECT
'overall' as metric_level
,'count of cid' as frequency_type
,'all advertisers' as advertiser_name
,'all campaigns' as campaign_name
,CASE WHEN impressions_served>10 then '10+'
when impressions_served between 6 and 10 then '06-10'
else concat('0',impressions_served) end as exposure_frequency
,count(DISTINCT cid) as targeted_customers
from user_lvl_freq_cid
group by 5
union all
SELECT
'overall' as metric_level
,'count of rampid' as frequency_type
,'all advertisers' as advertiser_name
,'all campaigns' as campaign_name
,CASE WHEN impressions_served>10 then '10+'
when impressions_served between 6 and 10 then '06-10'
else concat('0',impressions_served) end as exposure_frequency
,count(DISTINCT rmn_rampid) as targeted_customers
from user_lvl_freq_rampid
group by 5
)
select
metric_level
,frequency_type
,advertiser_name
,campaign_name
,exposure_frequency
,targeted_customers
from combined_dataset5. Frequency Analysis: What is the optimal frequency to deliver my campaigns?
This query provides insights into the performance and effectiveness of advertising campaigns and helps you identify the optimal frequency to deliver campaigns. By segmenting by frequency of user exposure to ads, analyzing metrics such as the number of users reached, conversions, gross revenue, and the impression volume across different frequency buckets, you can refine targeting strategies and optimize ad spend. This query applies last touch attribution using a custom attribution window.
Runtime parameters (highlighted in SQL):
click_attribution_window (Integer)
imp_attribution_window (Integer)
Partition parameters:
Exposure Start and End Dates
Conversion Start and End Dates
-- What is the optimal frequency to deliver my campaigns?
with traffic AS (
SELECT
@exposures.@cid as pub_cid,
@pubmap.@rampid as pub_rampid,
@exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name,
@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name,
@exposures.@event_type as event_type,
unix_timestamp(@exposures.@event_timestamp) AS event_timestamp_UNIX,
@exposures.@event_id as event_id
FROM @exposures
join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid
where
@exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
conversion AS (
SELECT
a.transaction_id,
a.gross_amt,
a.partner_cid as partner_cid,
@partnermap.@rampid as partner_rampid,
a.conversion_timestamp_UNIX as conversion_timestamp_UNIX
FROM
(select @conversions.@transaction_id as transaction_id, @conversions.@cid as partner_cid,
unix_timestamp(@conversions.@conversion_timestamp) as conversion_timestamp_UNIX,
sum(@conversions.@gross_amt) as gross_amt from @conversions group by 1,2,3) a
join @partnermap on a.partner_cid = @partnermap.@cid
where
a.partner_cid IS NOT NULL and @partnermap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @partnermap.@rampid is not null and @partnermap.@rampid != '0' and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
matched_latency AS (
SELECT
c.transaction_id,
t.event_id,
t.pub_cid,
t.advertiser_name,
t.campaign_name,
(case when t.event_type = 'click' then 1 else 2 end) AS match_type,
(conversion_timestamp_UNIX - event_timestamp_UNIX) / 86400 AS match_age,
max(c.gross_amt) as gross_amt
FROM
conversion c
JOIN traffic t ON c.partner_rampid = t.pub_rampid
group by 1,2,3,4,5,6,7),
first_ranked AS (
SELECT
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
---transaction_id,
event_id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(
PARTITION BY transaction_id
ORDER BY match_age DESC, match_type DESC) AS match_rank,
gross_amt,
pub_cid
FROM
matched_latency
WHERE
(match_type=1 AND match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @click_attribution_window)
OR (match_type=2 AND match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @imp_attribution_window)
),
last_ranked AS (
SELECT
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
transaction_id,
event_id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(
PARTITION BY transaction_id
ORDER BY
match_age ASC, -- last touch
match_type ASC
) AS match_rank,
gross_amt,
pub_cid
FROM
matched_latency
WHERE
(match_type=1 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @click_attribution_window)
OR (match_type=2 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @imp_attribution_window)
),
attributed_conv as (
SELECT
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
pub_cid,
count(distinct transaction_id) as conversions,
sum(gross_amt) as gross_amt
from last_ranked
WHERE match_rank = 1
group by 1,2,3
),
impression_users as (
select
@exposures.@cid as pub_cid,
@exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name,
@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name,
count(distinct @exposures.@event_id) as uc_imps
FROM @exposures
left join @pubmap on @pubmap.@cid = @exposures.@cid
where
@exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'
group by 1,2,3
),
impression_frequency as (
select pub_cid, advertiser_name, campaign_name,
case
when uc_imps = 1 then '01'
when uc_imps = 2 then '02'
when uc_imps = 3 then '03'
when uc_imps = 4 then '04'
when uc_imps = 5 then '05'
when uc_imps = 6 then '06'
when uc_imps = 7 then '07'
when uc_imps = 8 then '08'
when uc_imps = 9 then '09'
when uc_imps = 10 then '10'
when uc_imps = 11 then '11'
when uc_imps = 12 then '12'
when uc_imps = 13 then '13'
when uc_imps = 14 then '14'
when uc_imps = 15 then '15'
when uc_imps = 16 then '16'
when uc_imps = 17 then '17'
when uc_imps = 18 then '18'
when uc_imps = 19 then '19'
when uc_imps >= 20 and uc_imps <= 29 then '20-29'
when uc_imps >= 30 and uc_imps <= 39 then '30-39'
when uc_imps >= 40 and uc_imps <= 49 then '40-49'
when uc_imps >= 50 and uc_imps <= 59 then '50-59'
when uc_imps >= 60 and uc_imps <= 69 then '60-69'
when uc_imps >= 70 and uc_imps <= 79 then '70-79'
when uc_imps >= 80 and uc_imps <= 89 then '80-89'
when uc_imps >= 90 and uc_imps <= 99 then '90-99'
else 'Above 100' end as frequency_buckets,
uc_imps
from impression_users
)
select
i.advertiser_name,
i.campaign_name,
i.frequency_buckets,
count(distinct i.pub_cid) as imp_users,
coalesce(count(distinct c.pub_cid), 0) as con_users,
coalesce(SUM(c.conversions), 0) as conversions,
coalesce(sum(c.gross_amt),0) as gross_amt,
sum(i.uc_imps) as impressions
from impression_frequency i
left join attributed_conv c
USING (campaign_name, advertiser_name, pub_cid)
group by 1,2,34. Latency Analysis: How long does it take for a user to convert after first touch and last touch?
This query analyzes the impact of different touchpoints in a marketing campaign by determining the time it takes for users to convert after their first or last interaction with the advertiser. By segmenting users based on the days until conversion and associating it with either the first or last touch, you can gain insights into the effectiveness of your marketing strategy over time, optimizing campaigns for better performance.
Runtime parameters (highlighted in SQL):
click_attribution_window (Integer)
imp_attribution_window (Integer)
Partition parameters:
Exposure Start and End Dates
Conversion Start and End Dates
-- How long does it take for a user to convert after first touch and last touch?
with traffic AS (
SELECT
@exposures.@cid as pub_cid,
@pubmap.@rampid as pub_rampid,
@exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name,
@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name,
@exposures.@event_type as event_type,
unix_timestamp(@exposures.@event_timestamp) AS event_timestamp_UNIX,
@exposures.@event_id as event_id
FROM @exposures
join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid
where
@exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
conversion AS (
SELECT
a.transaction_id,
a.gross_amt,
a.partner_cid as partner_cid,
@partnermap.@rampid as partner_rampid,
a.conversion_timestamp_UNIX as conversion_timestamp_UNIX
FROM
(select @conversions.@transaction_id as transaction_id, @conversions.@cid as partner_cid,
unix_timestamp(@conversions.@conversion_timestamp) as conversion_timestamp_UNIX, sum(@conversions.@gross_amt) as gross_amt from @conversions group by 1,2,3) a
join @partnermap on a.partner_cid = @partnermap.@cid
where
a.partner_cid IS NOT NULL and @partnermap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @partnermap.@rampid is not null and @partnermap.@rampid != '0' and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
matched_latency AS (
SELECT
c.transaction_id,
t.event_id,
t.pub_cid,
t.advertiser_name,
t.campaign_name,
(case when t.event_type = 'click' then 1 else 2 end) AS match_type,
(conversion_timestamp_UNIX - event_timestamp_UNIX) / 86400 AS match_age,
max(c.gross_amt) as gross_amt
FROM
conversion c
JOIN traffic t ON c.partner_rampid = t.pub_rampid
group by 1,2,3,4,5,6,7),
first_ranked AS (
SELECT
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
transaction_id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(
PARTITION BY transaction_id
ORDER BY
match_age DESC, -- first touch
match_type ASC
) AS match_rank,
match_age,
match_type,
gross_amt,
pub_cid
FROM
matched_latency
WHERE
(match_type=1 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @click_attribution_window)
OR (match_type=2 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @imp_attribution_window)
),
last_ranked AS (
SELECT
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
transaction_id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(
PARTITION BY transaction_id
ORDER BY
match_age ASC, -- last touch
match_type ASC
) AS match_rank,
match_age,
match_type,
gross_amt,
pub_cid
FROM
matched_latency
WHERE
(match_type=1 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @click_attribution_window)
OR (match_type=2 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @imp_attribution_window)
),
final_ranked as (
(Select
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
( CASE
WHEN match_age > 0 AND match_age <= 1 THEN '01 | < 1 DAY'
WHEN match_age <= 2 THEN '02 | 1 - 2 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 3 THEN '03 | 2 - 3 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 4 THEN '04 | 3 - 4 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 5 THEN '05 | 4 - 5 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 6 THEN '06 | 5 - 6 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 7 THEN '07 | 6 - 7 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 8 THEN '08 | 7 - 8 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 9 THEN '09 | 8 - 9 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 10 THEN '10 | 9 - 10 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 11 THEN '11 | 10 - 11 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 12 THEN '12 | 11 - 12 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 13 THEN '13 | 12 - 13 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 14 THEN '14 | 13 - 14 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 20 THEN '15 | 15 - 20 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 25 THEN '16 | 21 - 25 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 30 THEN '17 | 26 - 30 DAYS'
ELSE '18 | 30+ DAYS'
END
) AS time_to_conversion,
'FT - First Touch' as touch_type,
SUM(gross_amt) as gross_amt,
COUNT(DISTINCT pub_cid) as converted_users
from first_ranked
WHERE match_rank = 1
GROUP BY 1,2,3)
UNION ALL
(Select
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
( CASE
WHEN match_age > 0 AND match_age <= 1 THEN '01 | < 1 DAY'
WHEN match_age <= 2 THEN '02 | 1 - 2 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 3 THEN '03 | 2 - 3 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 4 THEN '04 | 3 - 4 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 5 THEN '05 | 4 - 5 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 6 THEN '06 | 5 - 6 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 7 THEN '07 | 6 - 7 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 8 THEN '08 | 7 - 8 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 9 THEN '09 | 8 - 9 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 10 THEN '10 | 9 - 10 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 11 THEN '11 | 10 - 11 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 12 THEN '12 | 11 - 12 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 13 THEN '13 | 12 - 13 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 14 THEN '14 | 13 - 14 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 20 THEN '15 | 15 - 20 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 25 THEN '16 | 21 - 25 DAYS'
WHEN match_age <= 30 THEN '17 | 26 - 30 DAYS'
ELSE '18 | 30+ DAYS'
END
) AS time_to_conversion,
'LT - Last Touch' as touch_type,
SUM(gross_amt) as gross_amt,
COUNT(DISTINCT pub_cid) as converted_users
from last_ranked
WHERE match_rank = 1
GROUP BY 1,2,3)
ORDER BY 1,2,3
)
Select
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
time_to_conversion,
touch_type,
sum(gross_amt) as gross_amt,
sum(converted_users) as converted_users
from final_ranked
group by 1,2,3,4
3. Linear Attribution: What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on linear attribution with custom attribution window?
This query applies a linear attribution model, where credit for a conversion is distributed equally across all touchpoints associated with a transaction. By calculating the attributed revenue and conversions for each campaign, this approach provides a balanced view of how different marketing efforts contribute to conversions, helping you make informed decisions about resource allocation across campaigns.
Runtime parameters (highlighted in SQL):
click_attribution_window (Integer)
imp_attribution_window (Integer)
Partition parameters:
Exposure Start and End Dates
Conversion Start and End Dates
-- What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on linear attribution with custom attribution window? with traffic AS ( SELECT @exposures.@cid as pub_cid, @pubmap.@rampid as pub_rampid, @exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name, @exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name, @exposures.@event_type as event_type, unix_timestamp(@exposures.@event_timestamp) AS event_timestamp_UNIX ---@exposures.@event_id FROM @exposures join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid where @exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'), conversion AS ( SELECT a.transaction_id, a.gross_amt, a.partner_cid as partner_cid, @partnermap.@rampid as partner_rampid, a.conversion_timestamp_UNIX as conversion_timestamp_UNIX FROM (select @conversions.@transaction_id as transaction_id, @conversions.@cid as partner_cid, unix_timestamp(@conversions.@conversion_timestamp) as conversion_timestamp_UNIX, sum(@conversions.@gross_amt) as gross_amt from @conversions group by 1,2,3) a join @partnermap on a.partner_cid = @partnermap.@cid where a.partner_cid IS NOT NULL and @partnermap.@cid IS NOT NULL and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @partnermap.@rampid is not null and @partnermap.@rampid != '0' and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'), matched_latency AS ( SELECT c.transaction_id, ---t.event_id, t.pub_cid, t.advertiser_name, t.campaign_name, (case when t.event_type = 'click' then 1 else 2 end) AS match_type, (conversion_timestamp_UNIX - event_timestamp_UNIX) / 86400 AS match_age, max(c.gross_amt) as gross_amt FROM conversion c JOIN traffic t ON c.partner_rampid = t.pub_rampid group by 1,2,3,4,5,6), linear as ( SELECT advertiser_name, campaign_name, transaction_id, pub_cid, gross_amt / count(campaign_name) over (partition by transaction_id) as attributed_amt, 1 / count(campaign_name) over (partition by transaction_id) as attributed_conv from matched_latency WHERE (match_type=1 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @click_attribution_window) OR (match_type=2 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @imp_attribution_window) ) Select advertiser_name, campaign_name, 'Linear' as attribution_model, SUM(attributed_amt) as attributed_gross_amt, sum(attributed_conv) as attributed_conversions from linear GROUP BY 1,2,3
2. Last Touch Attribution: What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on last touch with the custom attribution window?
This query implements a last-touch attribution model, where 100% of the credit for a conversion is given to the last interaction the user had before converting. By aggregating the gross amount, conversion count, and unique converters for each campaign, this query provides insights into the effectiveness of the final touchpoint in driving conversions, helping you optimize your strategies based on the last interaction before a sale.
Runtime parameters (highlighted in SQL):
click_attribution_window (Integer)
imp_attribution_window (Integer)
Partition parameters:
Exposure Start and End Dates
Conversion Start and End Dates
-- What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on last touch with the custom attribution window?
with traffic AS (
SELECT
@exposures.@cid as pub_cid,
@pubmap.@rampid as pub_rampid,
@exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name,
@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name,
@exposures.@event_type as event_type,
unix_timestamp(@exposures.@event_timestamp) AS event_timestamp_UNIX,
@exposures.@event_id as event_id
FROM @exposures
join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid
where
@exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
conversion AS (
SELECT
a.transaction_id,
a.gross_amt,
a.partner_cid as partner_cid,
@partnermap.@rampid as partner_rampid,
a.conversion_timestamp_UNIX as conversion_timestamp_UNIX
FROM
(select @conversions.@transaction_id as transaction_id, @conversions.@cid as partner_cid,
unix_timestamp(@conversions.@conversion_timestamp) as conversion_timestamp_UNIX,
sum(@conversions.@gross_amt) as gross_amt from @conversions group by 1,2,3) a
join @partnermap on a.partner_cid = @partnermap.@cid
where
a.partner_cid IS NOT NULL and @partnermap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @partnermap.@rampid is not null and @partnermap.@rampid != '0' and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
matched_latency AS (
SELECT
c.transaction_id,
t.event_id,
t.pub_cid,
t.advertiser_name,
t.campaign_name,
(case when t.event_type = 'click' then 1 else 2 end) AS match_type,
(conversion_timestamp_UNIX - event_timestamp_UNIX) / 86400 AS match_age,
max(c.gross_amt) as gross_amt
FROM
conversion c
JOIN traffic t ON c.partner_rampid = t.pub_rampid
group by 1,2,3,4,5,6,7),
last_ranked AS (
SELECT
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
transaction_id,
--impression_id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(
PARTITION BY transaction_id
ORDER BY
match_age ASC, -- last touch
match_type ASC
) AS match_rank,
gross_amt,
pub_cid
FROM
matched_latency
WHERE
(match_type=1 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @click_attribution_window)
OR (match_type=2 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @imp_attribution_window)
)
Select
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
'Last Touch' as attribution_model,
SUM(gross_amt) as attributed_gross_amt,
count(distinct transaction_id) as attributed_conversions
from last_ranked
WHERE match_rank = 1
GROUP BY 1,2,3
1. First Touch Attribution: What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on first touch with the custom attribution window?
This query applies a first-touch attribution model, where the entire credit for a conversion is assigned to the first interaction a user had with the campaign. By summing the gross amount, conversion count, and unique converters for each campaign, this analysis helps you understand the impact of the initial touchpoint in driving conversions, allowing for strategic optimizations to attract and engage potential customers right from their first interaction.
Runtime parameters (highlighted in SQL):
click_attribution_window (Integer)
imp_attribution_window (Integer)
Partition parameters:
Exposure Start and End Dates
Conversion Start and End Dates
-- What is the attributed revenue of my campaign based on first touch with the custom attribution window?
with traffic AS (
SELECT
@exposures.@cid as pub_cid,
@pubmap.@rampid as pub_rampid,
@exposures.@advertiser_name as advertiser_name,
@exposures.@campaign_name as campaign_name,
@exposures.@event_type as event_type,
unix_timestamp(@exposures.@event_timestamp) as event_timestamp_UNIX,
@exposures.@event_id as event_id
FROM @exposures
join @pubmap on @exposures.@cid = @pubmap.@cid
where
@exposures.@cid IS NOT NULL and @pubmap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @pubmap.@rampid is not null and @pubmap.@rampid != '0' and @pubmap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
conversion AS (
SELECT
a.transaction_id,
a.gross_amt,
a.partner_cid as partner_cid,
@partnermap.@rampid as partner_rampid,
a.conversion_timestamp_UNIX as conversion_timestamp_UNIX
FROM
(select @conversions.@transaction_id as transaction_id, @conversions.@cid as partner_cid,
unix_timestamp(@conversions.@conversion_timestamp) as conversion_timestamp_UNIX,
sum(@conversions.@gross_amt) as gross_amt from @conversions group by 1,2,3) a
join @partnermap on a.partner_cid = @partnermap.@cid
where
a.partner_cid IS NOT NULL and @partnermap.@cid IS NOT NULL
and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNKNOWN' and @partnermap.@rampid is not null and @partnermap.@rampid != '0' and @partnermap.@rampid != 'UNMATCHED'),
matched_latency AS (
SELECT
c.transaction_id,
t.event_id,
t.pub_cid,
t.advertiser_name,
t.campaign_name,
(case when t.event_type = 'click' then 1 else 2 end) AS match_type,
(conversion_timestamp_UNIX - event_timestamp_UNIX) / 86400 AS match_age,
max(c.gross_amt) as gross_amt
FROM
conversion c
JOIN traffic t ON c.partner_rampid = t.pub_rampid
group by 1,2,3,4,5,6,7),
first_ranked AS (
SELECT
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
transaction_id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(
PARTITION BY transaction_id
ORDER BY
match_age DESC, -- first touch
match_type ASC
) AS match_rank,
match_age,
match_type,
gross_amt,
pub_cid
FROM
matched_latency
WHERE
(match_type=1 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @click_attribution_window)
OR (match_type=2 and match_age BETWEEN 0 AND @imp_attribution_window)
)
Select
advertiser_name,
campaign_name,
'First Touch' as attribution_model,
SUM(gross_amt) as attributed_gross_amt,
count(distinct transaction_id) as attributed_conversions
from first_ranked
WHERE match_rank = 1
GROUP BY 1,2,3
Media Intelligence FAQs
How do I apply Kmin/Noise to the questions in the clean room?
When you edit the Media Intelligence template, you can adjust the data control parameters for all brands you’ll work with. After you generate a specific clean room for a brand, you can then customize the data control parameters for that specific brand.
What’s the best and easiest way for me to set up our data?
The best and easiest way to set up your data is to have one exposures dataset containing all of your exposure data so that you only have to connect that dataset once. After you generate a clean room for a brand, you can then easily filter that dataset so that the brand is only able to access the data that is relevant to them.
What is the ideal formatting of the fields in our publisher datasets?
See "Format Your Clean Room Data" for information on formatting your exposures dataset and publisher audience dataset.